AI in QA testing is changing what testers do daily, but it's creating opportunity rather than obsolescence for professionals who adapt.
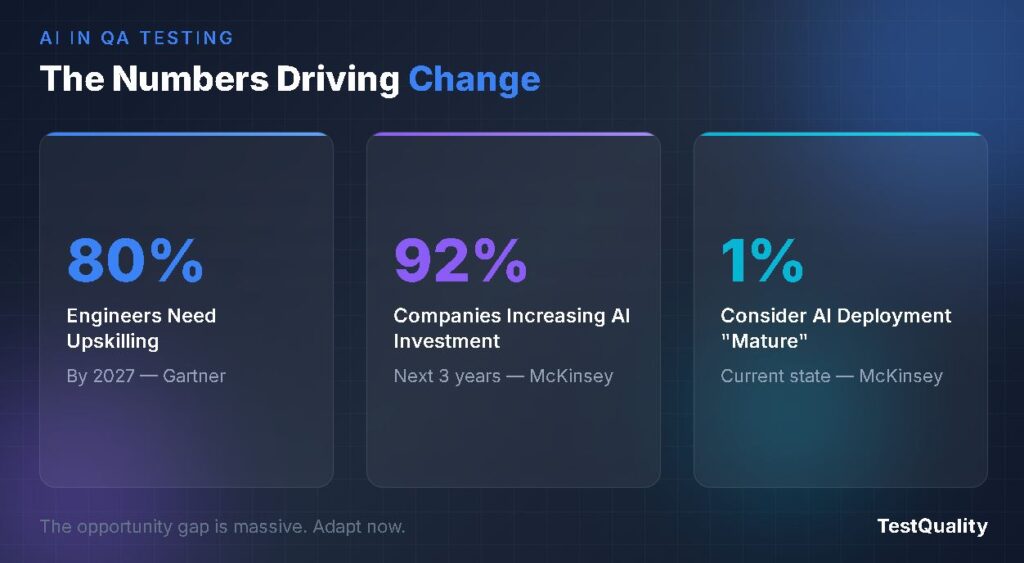
- Gartner predicts 80% of the engineering workforce will need to upskill by 2027 as AI transforms software roles.
- AI test case builders handle repetitive tasks like script generation and maintenance, freeing QA professionals for strategic work.
- The most successful teams are adopting AI-human collaboration in testing rather than viewing automation as a replacement.
QA leads and engineers who develop AI fluency now will command higher salaries and more influential positions in the years ahead.
With AI-powered tools now capable of generating test cases, predicting failures, and maintaining scripts autonomously, QA professionals face a legitimate question: where do humans fit in this equation? According to Gartner, generative AI will require 80% of the engineering workforce to upskill through 2027. That statistic alone signals the magnitude of change underway.
But here's what the headline-grabbing predictions often miss: AI in QA testing isn't eliminating roles. It's reshaping them. The engineers and leads who understand this distinction are positioning themselves for career acceleration rather than displacement. Modern test management platforms now incorporate AI capabilities that transform how teams approach quality assurance, making the human-AI partnership more productive than either could be alone.
This guide cuts through the noise to answer the question QA professionals are actually asking: is AI something to fear or something to master?
What Are AI Test Case Builders Changing About QA Work?
AI test case builders analyze requirements, user stories, and existing code to automatically generate test scenarios that would take humans hours to create manually. These tools identify edge cases, suggest coverage gaps, and produce test scripts based on patterns they've learned from millions of test suites.
The immediate impact hits the most time-consuming parts of QA work. Test case creation, which traditionally consumes significant portions of a tester's week, can now happen in minutes. Maintenance tasks that require updating hundreds of scripts after UI changes get handled by self-healing mechanisms that adapt automatically. Regression testing cycles that once blocked releases for days now run continuously in the background.

Where Automation Excels
AI shines brightest in pattern recognition and repetitive execution. Consider what these systems handle well: generating boilerplate test structures, identifying common input combinations, flagging contradictions in requirements documents, and maintaining test scripts as applications evolve. The technology excels at scale problems that would overwhelm human testers working manually.
The job change in QA becomes apparent when you examine daily workflows. Testers who previously spent mornings writing basic test cases now spend that time reviewing AI-generated scenarios and adding the contextual knowledge that machines can't replicate. The work shifts from creation to curation and strategic enhancement.

What Machines Still Can't Do
AI test case builders operate on patterns and probabilities. They don't understand your users' actual frustrations, your business's risk tolerance, or the subtle ways a feature might fail to deliver value even when it technically works correctly. They can't feel the intuition that tells an experienced tester something seems off about a particular flow.
The technology predicts what looks right based on training data. It doesn't grasp what is right for your specific product, market position, or user expectations. That gap is where human testers remain irreplaceable.
Is AI in QA Testing a Threat or a Tool?
AI will replace QA professionals whose work consists primarily of repetitive tasks that don't require critical thinking. If your daily responsibilities involve executing the same test scripts, logging basic bugs, and producing status reports without strategic input, that work is already being automated.
But here's the flip side that often gets lost in alarmist coverage. McKinsey research shows that 92% of companies plan to increase their AI investments over the upcoming years, while only 1% describe their current deployment as mature. This gap between investment and implementation creates demand for professionals who can bridge the divide between AI capabilities and practical testing needs.
The Threat Perspective
The concern isn't unfounded. Teams that previously needed ten testers for comprehensive coverage might accomplish the same work with three or four people augmented by AI tools. Entry-level positions focused on manual test execution face the most pressure, as these tasks offer the clearest automation opportunities.
Organizations also face real risks from over-reliance on AI-generated tests. Machines can produce thousands of test cases that all pass while missing the one scenario that actually matters to users. Speed without judgment creates technical debt that compounds over time.
The Tool Perspective
The more compelling narrative positions AI in QA testing as leverage rather than replacement. QA professionals who learn to direct AI tools multiply their impact. Instead of writing individual test cases, they architect testing strategies and review machine-generated coverage for gaps only human insight can identify.
This perspective aligns with what's happening in practice. Companies aren't laying off their testing teams wholesale. They're restructuring roles to emphasize the analytical and strategic skills that AI enhances rather than replaces. The professionals who adapt are finding their work more interesting, more impactful, and better compensated.

How Are QA Roles Evolving in the Age of Automation?
The shift from manual execution to strategic oversight is the most prominent job change in QA since the introduction of automated testing frameworks. New positions are emerging that didn't exist five years ago, while traditional roles are absorbing responsibilities that require deeper technical and business acumen.
Emerging QA Role Categories
Several distinct career paths are crystallizing as organizations integrate AI into their testing processes:
- AI Test Architects design and implement AI-powered testing strategies, selecting appropriate tools, defining automation boundaries, and ensuring AI-generated tests align with business objectives.
- Quality Engineers evolve beyond traditional QA to own end-to-end quality outcomes, combining testing expertise with development skills and AI tool proficiency.
- Test Automation Specialists focus on building and maintaining the infrastructure that connects AI tools to development pipelines, ensuring smooth data flow between systems.
- Human-in-the-Loop Validators specialize in reviewing AI-generated outputs, providing the contextual judgment that ensures machine-created tests actually serve user needs.
What Organizations Expect Now
Companies hiring QA professionals in 2026 expect candidates to demonstrate familiarity with AI-assisted testing tools. The baseline has shifted. Knowing how to write test cases manually remains valuable, but knowing how to leverage AI in QA testing to write better test cases faster has become the differentiator.
Integrating AI capabilities into existing workflows requires professionals who understand both traditional test automation approaches and emerging AI methodologies. The most valuable team members bridge these worlds, translating between what AI can theoretically do and what actually works in production environments.
What Skills Do QA Professionals Need to Thrive?
Surviving the AI transition requires intentional skill development. The most important capabilities are the distinctly human competencies that AI struggles to replicate.
Strategic and Analytical Capabilities
Risk assessment moves to the forefront. AI can generate thousands of test scenarios, but determining which ones actually matter requires understanding business context, user behavior, and failure consequences. QA professionals who can prioritize become more valuable as test volume increases.
Systems thinking matters more than individual test creation. Understanding how components interact, where failures cascade, and which integrations carry the highest risk positions testers as strategic advisors rather than execution resources. This big-picture perspective can't be automated.
Technical Fluency
Prompt engineering has become a practical skill for QA teams. Knowing how to communicate with AI tools to get useful outputs separates efficient testers from those who waste time on poorly scoped automation attempts. The ability to iterate on prompts and refine the behavior of AI in QA testing is immediately applicable.
Familiarity with modern development practices remains essential. AI-human collaboration in testing works best when QA professionals understand CI/CD pipelines, version control workflows, and the development tools their teams use daily. Platforms that integrate natively with GitHub and Jira provide natural environments for this collaboration.
Communication and Influence
The ability to translate between technical and business stakeholders becomes more valuable as testing generates more data. QA professionals who can explain what AI-generated metrics mean for business outcomes position themselves as advisors rather than service providers.
Advocating for quality investment requires persuasion skills. When AI makes testing faster, some organizations will push for reduced QA headcount. Professionals who can articulate why human oversight remains essential protect both quality outcomes and their teams.
How Does AI-Human Collaboration in Testing Actually Work?
Effective partnerships between human testers and AI tools follow recognizable patterns. Understanding these collaboration models helps teams implement AI without losing the contextual judgment that makes testing valuable.
The Division of Labor
The most successful teams establish clear boundaries between AI responsibilities and human oversight. The table below illustrates how leading organizations typically divide the activities of humans and AI in QA testing:
| Activity | AI Responsibility | Human Responsibility |
| Test case generation | Creates initial scenarios from requirements | Reviews for business relevance and completeness |
| Script maintenance | Updates locators and handles UI changes | Validates that updates preserve test intent |
| Regression execution | Runs full suites continuously | Analyzes failures and determines root causes |
| Coverage analysis | Identifies untested code paths | Prioritizes gaps based on risk assessment |
| Bug triage | Categorizes and groups similar issues | Determines severity and business impact |
| Test data creation | Generates synthetic datasets | Ensures data reflects realistic user scenarios |
This division leverages AI's strengths in speed and scale while preserving human judgment where it matters most. Neither party works in isolation; the collaboration produces better outcomes than either could achieve alone.
Implementation Patterns That Work
Organizations finding success with AI-human collaboration in testing typically start narrow and expand gradually. They identify specific pain points where AI can provide immediate value, implement tools to address those needs, and then evaluate results before broadening their scope.
AI-powered test planning often serves as an entry point because it delivers visible benefits quickly. Teams can experience AI-assisted workflows without fully committing to automation across all testing activities. This measured approach builds confidence while limiting risk.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Over-automation creates its own problems. Teams that hand too much responsibility to AI without adequate human review often discover their test suites have grown comprehensive but irrelevant. Quantity doesn't equal quality in testing, and AI systems optimize for coverage metrics that may not align with actual quality outcomes.
Insufficient training undermines AI tool investments. Teams need time to learn how to effectively work with new capabilities. Organizations that rush implementation without allowing for learning curves often abandon tools prematurely or use them ineffectively.

What Does the Future Hold for QA Automation?
The trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated AI capabilities paired with evolving human roles. QA automation will handle more tasks autonomously, but the need for human strategic oversight will grow rather than diminish.
Emerging Capabilities
Agentic AI is the next frontier in testing automation. These systems will autonomously handle multi-step processes, making decisions and taking actions across complex workflows. Early implementations already demonstrate AI agents that can explore applications, identify bugs, and suggest fixes without human intervention at each step.
Predictive quality assurance moves testing from reactive to proactive. Instead of finding bugs after they're created, AI systems will flag potential quality issues during development, before code even reaches testing environments. This shift-left approach changes when and how testing happens.
What Won't Change
The need for human judgment about what constitutes quality remains constant. Technology changes rapidly, but the fundamental challenge of ensuring software serves user needs persists. AI helps identify whether code works correctly; humans determine whether it works valuably.
Accountability stays with people. When AI-generated tests miss critical bugs, someone has to explain what went wrong and prevent recurrence. That responsibility can't be delegated to machines, which means human oversight remains essential regardless of how sophisticated automation becomes.

FAQ
Will AI completely replace QA engineers? No. AI will replace specific tasks, particularly repetitive test execution and basic script maintenance. However, the strategic, analytical, and contextual aspects of quality assurance require human judgment that AI can't replicate. The demand for QA professionals who can effectively leverage AI tools is actually increasing.
How quickly do I need to learn AI testing tools? The transition is happening now. Gartner projects that 80% of engineering professionals will need to upskill by 2027. Professionals who develop AI fluency within the next 12 to 18 months will have advantages in career advancement and compensation.
What's the first step for QA teams adopting AI tools? Start with a specific pain point rather than trying to automate everything at once. Test case generation often provides a good entry point because it delivers quick wins while allowing teams to develop familiarity with AI-assisted workflows. Measure results carefully before expanding the scope.
Can AI understand complex business requirements for testing? AI can parse and generate tests from written requirements, but it doesn't truly understand business context, user needs, or strategic priorities. Human oversight remains essential for ensuring AI-generated tests actually validate what matters to users and the business.
Build Your AI-Ready QA Career Now
The window for positioning yourself as an AI-augmented QA professional is open now, but it won't stay open indefinitely. The professionals who develop AI fluency early will shape how their organizations implement these tools. Those who wait will find themselves adapting to systems designed without their input.
Start by experimenting with AI test case generation in your current projects. Learn what these tools do well and where they need guidance. Develop your own prompt engineering skills and build familiarity with multiple AI-assisted testing platforms.
For teams ready to integrate AI-human collaboration into their workflows, TestQuality provides a modern test management platform with built-in AI capabilities, including TestStory.ai for intelligent test case generation. Start your free trial to experience how AI-powered testing can transform your QA processes.