Key Takeaways: Gherkin acceptance criteria transform user stories into executable specifications that bridge technical and business teams.
- Use Given-When-Then format for clear, testable conditions that eliminate ambiguity
- Focus on user behavior and outcomes rather than technical implementation details
- Implement collaborative writing practices involving product owners, developers, and QA teams
- Integrate acceptance criteria early in development to catch the 56% of defects that typically originate in requirements phases
Writing gherkin acceptance criteria has become essential for modern software development teams seeking to bridge the communication gap between business stakeholders and technical teams. The 2024 World Quality Report shows that over 60% of agile teams have adopted BDD practices to enhance collaboration and ensure software behaviors align with user needs.
What Are Gherkin Acceptance Criteria?
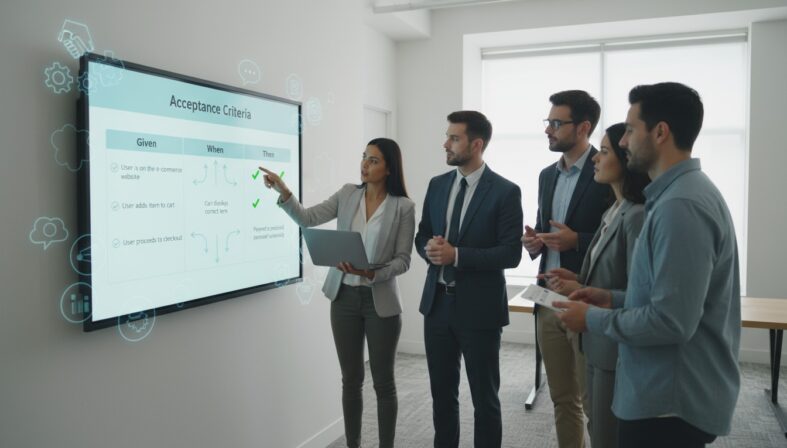
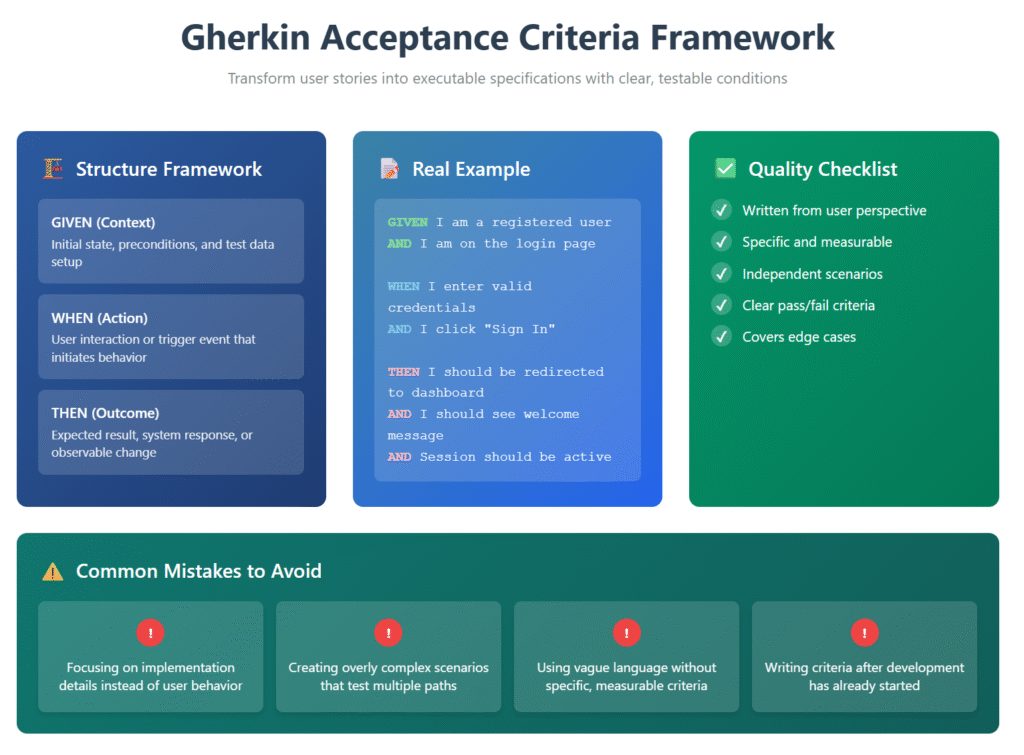
Gherkin acceptance criteria are structured specifications written in plain English using the Gherkin format that define exactly what conditions a user story must meet to be considered complete and acceptable. Unlike traditional acceptance criteria, these specifications follow a standardized Given-When-Then syntax that makes them both human-readable and executable by testing frameworks.
The gherkin format transforms vague requirements into precise, testable conditions. For example, instead of saying "users should be able to log in," gherkin acceptance criteria would specify:
Given I am a registered user with valid credentials
When I enter my email and password and click "Login"
Then I should be redirected to the dashboard
And I should see a welcome message with my name
This structured approach eliminates ambiguity and provides developers with clear implementation guidance while giving QA teams specific scenarios to verify.
Why Do Gherkin Acceptance Criteria Matter More Than Ever?
Software development teams face unprecedented pressure to deliver quality products quickly. Research shows that 56% of software defects are introduced during the requirements and design stages, making clear acceptance criteria crucial for preventing costly downstream issues.
Modern development practices have evolved beyond traditional documentation. Teams need living specifications that evolve with their products and remain executable throughout the development lifecycle. These structured criteria serve this dual purpose by providing both documentation and automated test foundations.
The rise of shift-left testing has made early requirement clarification even more critical. 68% of QA professionals now incorporate shift-left principles, emphasizing the importance of defining testable criteria before development begins.
Cross-functional collaboration has become standard practice, with teams needing shared understanding across diverse roles. Gherkin acceptance criteria provide a common language that product managers, developers, and testers can all understand and contribute to effectively.

How Do You Write Effective Gherkin Acceptance Criteria?
Creating effective acceptance specifications requires a systematic approach that balances clarity, completeness, and testability. The process involves understanding user needs, translating them into structured scenarios, and ensuring they provide sufficient guidance for implementation and testing.
Start with User Behavior Focus
Begin by identifying the specific user behavior or outcome your story addresses. Effective acceptance criteria describe what users can accomplish rather than how the system implements features. Focus on observable actions and results that stakeholders can validate.
Consider the user's mental model and workflow. What triggers their interaction with your feature? What do they expect to happen? What would constitute success from their perspective? This user-centric approach ensures your criteria capture actual value rather than technical specifications.
Apply the Given-When-Then Structure
The Given-When-Then structure provides a consistent framework for organizing acceptance criteria that eliminates ambiguity:
- Given establishes the initial context and preconditions
- When describes the specific action or trigger event
- Then defines the expected outcome or system response
- And/But can extend any section for additional conditions
Each element serves a distinct purpose in creating testable specifications. The Given section sets up test data and system state, When defines user interactions, and Then specifies verifiable results.
Ensure Independent and Atomic Scenarios
Each gherkin acceptance criteria scenario should be self-contained and executable independently. Avoid creating dependencies between scenarios, as this makes testing fragile and debugging difficult. If scenarios share setup requirements, consider using Background sections rather than creating interdependencies.
Atomic scenarios focus on testing one specific aspect of functionality. This granular approach makes it easier to identify the root cause when tests fail and enables teams to implement features incrementally.
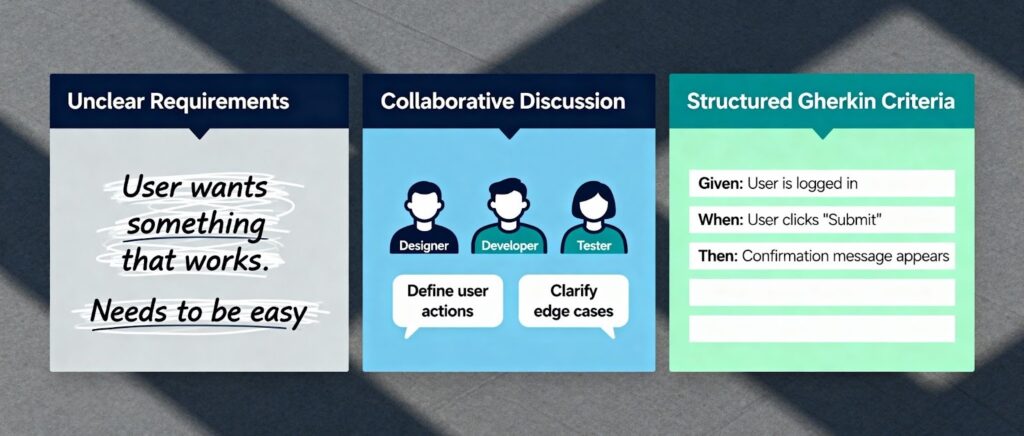
What Are the Essential Best Practices for Gherkin Acceptance Criteria?
Following established best practices ensures your acceptance criteria provide maximum value for development and testing activities while maintaining clarity for all stakeholders.
Write from the User's Perspective
Effective acceptance criteria always reflect the user's viewpoint rather than internal system processes. Use domain language that business stakeholders understand, avoiding technical implementation details. This approach keeps the focus on delivering user value rather than just completing technical tasks.
Frame scenarios in terms of user goals and outcomes. Instead of describing database operations or API calls, explain what the user experiences and achieves through their interactions with your software.
Make Criteria Specific and Measurable
Vague acceptance criteria create confusion and inconsistent implementations. Use specific values, timeframes, and conditions that leave no room for interpretation. Replace words like "quickly" with specific response times, or "many" with actual quantities.
According to Peacock Consulting research, well-written acceptance criteria should have clear pass/fail results that enable objective validation. This specificity supports automated testing and reduces subjective interpretations.
Keep Scenarios Simple and Focused
Each scenario should test one primary path or business rule. Complex scenarios that verify multiple conditions simultaneously become difficult to maintain and debug. Break complex workflows into multiple scenarios that each verify specific aspects of functionality.
Simple scenarios are easier for stakeholders to review and understand. They also provide better diagnostic information when tests fail, helping teams identify and resolve issues more efficiently.
Use Consistent Language and Terminology
Establish a shared vocabulary for your domain and use it consistently across all acceptance criteria. This ubiquitous language reduces confusion and ensures that terms mean the same thing to all team members. Document key terms and their definitions to support team alignment.
Consistency extends beyond individual projects to your broader product ecosystem. Teams working on related features should use compatible terminology to support integration and reduce cognitive overhead.
What Common Mistakes Should You Avoid When Writing Gherkin Acceptance Criteria?
Understanding common pitfalls helps teams develop more effective acceptance criteria and avoid time-consuming revisions during development.
Focusing on Implementation Rather Than Behavior
One frequent mistake involves describing how the system should work internally rather than what users experience. Acceptance criteria should specify expected behaviors without constraining implementation approaches. This separation allows developers flexibility while ensuring user needs are met.
For example, avoid criteria like "When the system calls the authentication API" and instead write "When I enter valid login credentials." The first approach couples tests to implementation details, while the second focuses on user interaction.
Creating Overly Complex Scenarios
Complex scenarios that test multiple conditions or user paths become difficult to understand and maintain. They also provide poor diagnostic information when failures occur. Break complex workflows into multiple focused scenarios that each verify specific aspects of functionality.
Clear, simple acceptance criteria significantly reduce misunderstandings within development teams and prevent costly rework that can derail project timelines and budgets.
Missing Edge Cases and Error Conditions
While happy path scenarios are important, comprehensive acceptance criteria must also address error conditions and boundary cases. Consider what happens when users provide invalid input, when systems are unavailable, or when data limits are exceeded.
Edge cases often reveal important design decisions that need stakeholder input. Addressing these scenarios early prevents surprise requirements during development and ensures robust implementations.
Writing Criteria Too Late in the Process
Acceptance criteria provide maximum value when written before development begins. Teams that add criteria during or after implementation miss opportunities to clarify requirements and often discover gaps that require rework.
The collaborative process of writing acceptance criteria often reveals requirements ambiguities and assumptions that need resolution. This discussion is most valuable before development resources are committed.
How Do Different Gherkin Acceptance Criteria Formats Compare?
Understanding various formats helps teams choose approaches that best fit their context and stakeholder needs.
| Format | Best Used For | Advantages | Considerations |
| Given-When-Then | Behavior scenarios | Clear structure, tool support | Can be verbose for simple rules |
| Rule-based statements | Business rules, constraints | Concise, easy to read | Less automation-friendly |
| Scenario outlines | Data-driven testing | Efficient for multiple inputs | Requires careful data design |
| Acceptance tables | Complex validations | Comprehensive coverage | Can become unwieldy |
The Given-When-Then format remains the most widely adopted approach because it provides excellent tool support and promotes clear thinking about user interactions. However, teams may benefit from mixing formats based on the nature of their requirements.
Consider your team's technical maturity and automation goals when selecting formats. Teams with strong automation practices typically prefer formats that translate directly into executable tests.
Which Tools Best Support Gherkin Acceptance Criteria Management?
Effective tool selection amplifies the benefits of well-written acceptance criteria by supporting collaboration, automation, and traceability throughout the development lifecycle.
Test Management Platforms
Modern AI-powered test management solutions go beyond basic storage to provide comprehensive support for structured acceptance criteria. Features now include intelligent collaborative editing, version control, and integration with agentic workflows. These platforms enable teams to maintain living documentation that evolves with their products, bridging the gap between static requirements and dynamic testing.
Leading solutions offer features like real-time collaboration, requirement traceability, and automated synchronization with development tools. This integration ensures that acceptance criteria remain current and actionable rather than becoming stale documentation.
Automation Framework Integration
Tools like Cucumber, SpecFlow, and Behave enable teams to execute gherkin acceptance criteria as automated tests. This capability transforms specifications into living documentation that validates system behavior continuously.
The key advantage lies in maintaining perfect alignment between specifications and implementation. When acceptance criteria serve as both documentation and tests, teams eliminate the common problem of documentation drift that undermines traditional approaches.
AI-Powered Enhancement for Acceptance Criteria
Modern development teams are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence to improve their acceptance criteria writing process. AI-powered tools can help teams generate comprehensive test scenarios, identify edge cases that human reviewers might miss, and ensure consistent language across acceptance criteria. These intelligent systems analyze existing criteria patterns and suggest improvements based on industry best practices.
Tools like TestStory.ai are revolutionizing this process, leveraging advanced LLMs to act as intelligent QA agents. These agents can analyze user story content to generate comprehensive Gherkin scenarios, suggest edge cases, and validate criteria completeness instantly. This allows teams to create effective acceptance criteria faster without leaving their collaborative environments.
Learn more about TestStory.ai
How Can Teams Implement Gherkin Acceptance Criteria Successfully?
Successful implementation requires more than just learning syntax – teams need processes that support collaboration and continuous improvement.
Establish Collaborative Writing Practices
The most effective acceptance criteria emerge from collaborative discussions involving product owners, developers, and testers. This "three amigos" approach ensures that criteria capture business intent while remaining technically feasible and testable.
Schedule regular refinement sessions where teams review and improve acceptance criteria based on implementation experience. These sessions help teams develop shared understanding and refine their approach over time.
Integrate with Development Workflows
Connect acceptance criteria directly to your development process by linking them to user stories, pull requests, and automated tests. This integration ensures that criteria remain visible and actionable throughout development.
Consider using acceptance criteria as definition-of-done gates that prevent features from advancing until all conditions are met. This approach reinforces the importance of meeting specified requirements and prevents incomplete implementations.
TestQuality’s AI-powered platform elevates these capabilities by allowing teams to leverage powerful QA agents. Users can create acceptance criteria collaboratively and then execute them effectively using TestStory.ai, which generates and runs test cases automatically from a chat interface. This integration allows for the analysis of test results 24/7, accelerating software quality for both human and AI-generated code.
TestQuality’s AI-powered platform TestStory.ai
Measure and Improve Criteria Quality
Track metrics like requirement clarity, defect rates, and rework frequency to assess the effectiveness of your acceptance criteria. Use this data to identify improvement opportunities and refine your writing practices.
Regularly review criteria that led to confusion or required clarification during development. These retrospectives help teams develop better practices and avoid recurring issues.
FAQ
What's the difference between user stories and structured acceptance criteria?
User stories describe what users want to accomplish and why, typically following the "As a [user], I want [feature] so that [benefit]" format. Gherkin acceptance criteria define the specific conditions that must be met for the user story to be considered complete, using the Given-When-Then structure to specify testable scenarios.
How many acceptance criteria should each user story have?
Most effective user stories have 1-3 acceptance criteria. If you find yourself writing 4 or more criteria, consider whether the story is too large and should be split into smaller, more focused stories. Each criterion should test a distinct aspect of the functionality.
Can gherkin acceptance criteria be automated without using BDD tools?
While gherkin acceptance criteria are designed to work with BDD frameworks like Cucumber, teams can benefit from the structured format even without automation tools. The clear Given-When-Then structure improves communication and testing regardless of automation approach.
How do you handle complex business rules in gherkin format?
Break complex rules into multiple simple scenarios rather than trying to capture everything in one criterion. Use scenario outlines for rules that apply across different data sets, and consider using rule keywords to group related scenarios under business rules.
Should acceptance criteria include non-functional requirements?
Yes, gherkin acceptance criteria should address relevant non-functional requirements like performance, security, and usability. Frame these requirements in terms of user-observable behavior, such as "Then the page should load within 3 seconds" or "Then I should see a confirmation that my data was encrypted."
Q: Can AI tools accurately generate Gherkin scenarios from raw requirements?
A: Yes, modern AI-powered tools have evolved beyond simple text generation to become context-aware QA agents. Solutions like TestStory.ai can analyze raw inputs—such as UI screenshots, wireframes, or brief user stories—to generate comprehensive Gherkin scenarios automatically. These agents excel at identifying overlooked edge cases and can instantly convert these criteria into executable test steps, significantly reducing manual boilerplate work while allowing QA professionals to focus on strategy and validation
Transform Your Testing Process with Clear Gherkin Acceptance Criteria
Mastering structured acceptance criteria transforms how teams collaborate on software requirements and dramatically improves the quality of delivered features. By focusing on user behavior, maintaining clear structure, and ensuring testability, teams create specifications that serve as both documentation and validation tools throughout the development lifecycle.
The investment in well-written acceptance criteria pays dividends through reduced rework, improved communication, and more reliable automated testing. Teams that adopt these practices consistently report better alignment between stakeholders and more predictable delivery outcomes.
Ready to revolutionize your team's approach to requirements and testing? Leverage TestQuality’s powerful QA agents to create and run test cases, and analyze test results automatically from a chat interface or your agentic workflows. Start your free trial today and experience how AI-powered QA can transform your development process."