Key Takeaways
Effective test automation in CI/CD requires strategic planning and the right integration approach to maximize both speed and quality.
- Early integration advantage: Teams implementing automation early in CI/CD pipelines achieve faster deployment cycles and improved development velocity through immediate feedback loops
- Strategic test selection: Focus on automating repetitive, high-value tests while maintaining manual testing for exploratory and usability scenarios
- Unified toolchain approach: Integrated platforms that unify test management with CI/CD workflows reduce tool sprawl, streamline processes, and improve team collaboration.
- Continuous optimization: Regular monitoring and refinement of automated test suites ensures sustained ROI and pipeline efficiency
Start with a clear automation strategy that aligns with your development velocity and quality goals.
The modern software landscape demands rapid delivery without compromising quality. The automation testing market is projected to reach $63.05 billion by 2032, reflecting widespread enterprise adoption of automated testing practices. This shift isn't just about speed—it's about building sustainable development practices that scale with business growth.
Implementing test automation in CI/CD pipelines represents one of the most significant improvements teams can make to their software delivery process. However, success requires more than simply adding automated tests to your build process. It demands strategic thinking about what to automate, when to run tests, and how to maintain quality as your system evolves.
Why Test Automation in CI/CD Matters Now
The automation testing market is experiencing explosive growth, projected to reach $63.05 billion by 2032 with a compound annual growth rate of 17.3%. This expansion reflects a fundamental shift in how organizations approach software quality and delivery speed.
DevOps adoption has accelerated significantly, with 51.8% of teams embracing these practices by 2024—a dramatic increase from just 16.9% in 2022. This transformation creates both opportunities and challenges for testing teams who must adapt their processes to support continuous integration and deployment workflows.
The integration of automation in DevOps environments offers compelling advantages. Teams can execute thousands of test cases across multiple platforms simultaneously, catch defects earlier in the development cycle, and maintain consistent quality standards even as development velocity increases. Most importantly, automation reduces the manual overhead that traditionally bottlenecked release cycles.
Building Your CI/CD Test Automation Foundation
Defining Clear Automation Objectives
Before implementing any automated testing solution, establish specific goals that align with your development process. Common objectives include reducing regression testing time, enabling continuous deployment, improving test coverage across environments, or supporting shift-left testing initiatives.

Your automation objectives should drive every subsequent decision about tools, frameworks, and team structure. Teams focused on rapid iteration might prioritize fast-running unit and integration tests, while those in regulated industries may emphasize comprehensive end-to-end validation and compliance reporting.
How Do You Assess Your Current Testing Landscape?
Evaluate existing manual testing processes to identify automation candidates. Not every test should be automated—focus on scenarios that are repetitive, time-consuming, and prone to human error. High-value automation targets typically include regression test suites, smoke tests for deployment validation, and data-driven scenarios with multiple input combinations.
Consider your team's technical capabilities and available resources. Developing a comprehensive test automation strategy requires careful planning around skill development, tool selection, and ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
Strategic Technology Stack Selection
The foundation of successful CI/CD test automation lies in selecting tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing development ecosystem. DevOps adoption has accelerated significantly, driving demand for reliable CI/CD integration platforms and automation frameworks.
Consider factors such as programming language compatibility, supported testing types, maintenance requirements, and long-term scalability. Your chosen framework should support unit testing for rapid feedback, API testing for service validation, and end-to-end testing for user experience verification.
Understanding CI/CD Test Automation Types
Unit Testing: The Foundation Layer
Unit tests form the base of the testing pyramid and provide the fastest feedback in your CI/CD pipeline. These tests validate individual components in isolation and should execute in milliseconds rather than minutes. Implement unit tests to run on every code commit, providing immediate feedback to developers about potential issues.
Effective unit testing strategies focus on critical business logic, edge cases, and integration points between components. Aim for high code coverage while avoiding tests that simply verify framework functionality or trivial implementations.
Integration Testing for System Validation
Integration tests verify that different components work together correctly and handle the complexity of modern distributed systems. These tests typically run after successful unit test execution and validate API contracts, database interactions, and service communication patterns.
Design integration tests to use test doubles or containerized services to ensure consistent execution across different environments. Focus on testing the integration points that are most likely to break due to changes in dependent services or configuration.
When Should You Use End-to-End Testing?
End-to-end tests simulate real user workflows and provide confidence that complete user journeys function correctly. While these tests offer high value, they require careful management due to their complexity and execution time.
Limit end-to-end tests to critical user paths and business-critical functionality. Use techniques like parallel execution and environment provisioning to minimize their impact on pipeline performance. Consider running comprehensive end-to-end suites on a scheduled basis rather than blocking every deployment.
Performance and Security Testing Integration
Modern CI/CD pipelines must address non-functional requirements alongside feature validation. Integrate performance testing to catch regression in application speed and resource utilization. Security testing should validate both known vulnerabilities and compliance requirements.
Implement these testing types as early as possible in your pipeline while balancing execution time against feedback speed. Use synthetic data and representative test environments to ensure reliable results without exposing production systems.
Step-by-Step CI/CD Test Automation Implementation
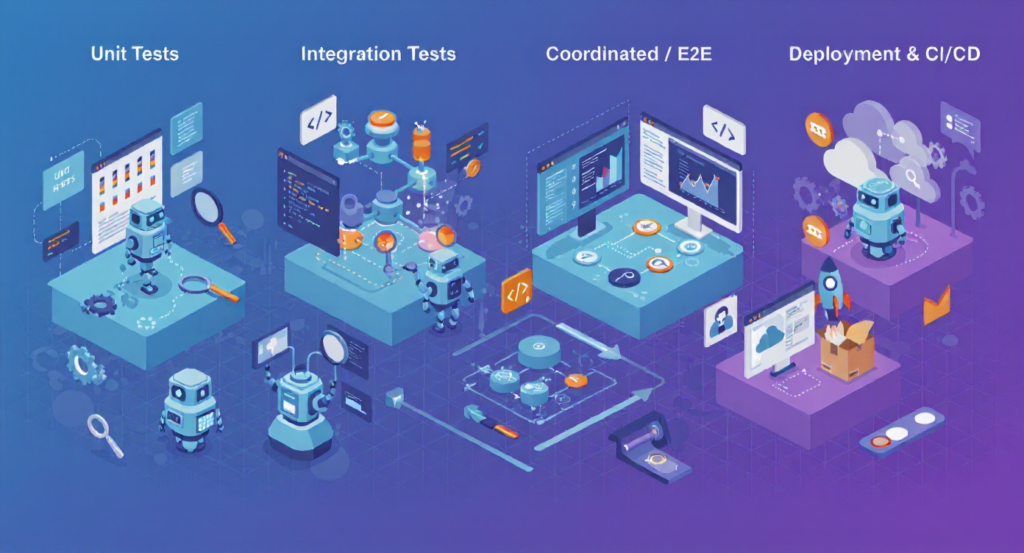
A visual representation of the different stages and types of testing within a CI/CD pipeline: Unit Tests, Integration Tests, Coordinated / E2E Tests, and Deployment & CI/CD.
Phase 1: Pipeline Integration Setup
Begin by integrating basic automated tests into your existing CI/CD pipeline. Start with unit tests that provide immediate feedback and establish the foundation for more complex testing scenarios. Configure your build system to fail fast when tests detect issues, preventing problematic code from advancing through your pipeline.
Establish clear conventions for test execution, result reporting, and failure handling. Your team needs consistent processes for interpreting test results and responding to failures across different testing types and environments.
Phase 2: Environment and Data Management
Reliable test automation requires consistent environments and representative test data. Implement infrastructure as code practices to ensure test environments match production configurations. Use containerization or virtualization to provide isolated, reproducible testing contexts.
Develop strategies for test data management that balance realism with privacy and security requirements. Consider using data masking, synthetic data generation, or snapshot-based approaches to provide consistent test scenarios without exposing sensitive information.
Phase 3: Advanced Automation Techniques
As your automation matures, implement advanced techniques like parallel test execution, dynamic test selection based on code changes, and intelligent failure analysis. These optimizations reduce pipeline execution time while maintaining comprehensive coverage.
Explore techniques like test impact analysis to run only tests affected by recent changes, reducing unnecessary execution time. Implement retry mechanisms for flaky tests while addressing underlying stability issues.
Phase 4: Monitoring and Optimization
Establish comprehensive monitoring for your test automation pipeline, tracking metrics like test execution time, failure rates, and coverage trends. Use this data to identify optimization opportunities and ensure your automation strategy delivers sustained value.
Platforms offering integrated dashboards and analytics can be instrumental in providing this real-time visibility.
Regular maintenance becomes critical as your test suite grows. Schedule periodic reviews to remove obsolete tests, update test data, and refactor automation code following the same standards applied to production code.
Essential CI/CD Test Automation Best Practices
Starting Small and Scaling Gradually
Implement automation incrementally rather than attempting to automate everything at once. Begin with your most stable and repetitive test scenarios, then expand coverage as your team develops expertise and confidence with automated testing tools.
Focus on achieving early wins that demonstrate the value of automation to stakeholders. Success with initial automation efforts builds support for expanding the program and investing in more sophisticated tooling.
Maintaining Test Independence and Reliability
Design automated tests to run independently without dependencies on test execution order or shared state. This approach enables parallel execution and makes tests more maintainable as your system evolves.
Address test flakiness immediately rather than accepting unreliable tests. Flaky tests undermine confidence in your automation and create noise that obscures real issues. Implement robust waits, proper test isolation, and stable test data management to improve reliability.
How Can You Optimize for Fast Feedback?
Structure your test execution to provide the fastest possible feedback on common issues. Run quick unit and integration tests first, followed by more comprehensive but slower end-to-end validation. This approach allows teams to identify and fix problems without waiting for complete test suite execution.
Consider implementing test result caching and smart test selection to reduce unnecessary execution time. Balance comprehensive coverage with practical pipeline performance requirements.
Quality Gates and Comprehensive Reporting
Implement quality gates that prevent code advancement when automated tests indicate problems. Establish clear criteria for different pipeline stages and ensure that test failures provide actionable information for developers.
Create comprehensive reporting that provides visibility into test results across different types and environments. Teams need clear dashboards showing test trends, coverage metrics, and failure analysis to maintain effective automation programs.
A unified test management solution facilitates this by centralizing all test data and offering customizable reporting.
Overcoming Common CI/CD Test Automation Challenges
| Challenge | Impact | Solution Strategy |
| Test Maintenance Overhead | High ongoing effort to update tests | Implement page object patterns, use stable locators, regular refactoring |
| Flaky Test Results | Reduced confidence in automation | Robust waits, proper test isolation, environment consistency |
| Slow Pipeline Execution | Delayed feedback and deployment bottlenecks | Parallel execution, test optimization, selective test running |
| Environment Inconsistencies | Unreliable test results across stages | Infrastructure as code, containerization, environment parity |
| Solution Measures | Limited team capability for automation development | Training programs, strategic tool selection aligning with team skills (e.g., platforms supporting diverse frameworks), gradual capability building. |
Managing Test Maintenance at Scale
As your automated test suite grows, maintenance becomes a significant challenge. Implement coding standards for test automation that mirror production code practices. Use design patterns like page objects for UI tests and maintain clear separation between test logic and test data.
Establish regular maintenance cycles to review and update test automation code. Treat test code as a first-class citizen in your codebase, applying the same review processes and quality standards used for production features.
Addressing Skills and Training Needs
Successful test automation requires a combination of testing expertise and development skills. Invest in training programs that help team members develop automation capabilities while maintaining their domain knowledge of the application under test.
Consider the balance between developing internal capabilities and leveraging external expertise. Some teams benefit from partnering with automation specialists during initial implementation while building long-term internal capacity.
Handling Complex Application Architectures
Modern applications often involve microservices, APIs, databases, and third-party integrations that complicate automation efforts. Develop testing strategies that address each architectural component while maintaining efficient execution.
Use service virtualization and test doubles to isolate components during testing. This approach enables reliable automation even when dependent services are unavailable or unreliable during test execution.
Tools and Frameworks for CI/CD Test Automation Success
Popular Automation Frameworks
The automation landscape offers numerous frameworks, each with specific strengths for different testing scenarios. Selenium remains popular for web application testing, while newer tools like Playwright gain adoption for their speed and reliability improvements.

For API testing, tools like Postman and REST Assured provide comprehensive capabilities for validating service contracts and data flows. Mobile testing benefits from frameworks like Appium that support cross-platform automation.
CI/CD Integration Tools
Jenkins continues to dominate CI/CD automation with its extensive plugin ecosystem and flexible configuration options. GitLab CI and GitHub Actions offer integrated approaches that combine version control with automation pipelines.
Choose tools that integrate naturally with your existing development workflow rather than forcing process changes. The best automation tools are those that your team actually uses consistently.
Test Management and Reporting Solutions
Effective test automation requires comprehensive test management capabilities that provide centralized visibility into results across different testing types and environments. Platforms that integrate directly with CI/CD pipelines are crucial, offering real-time reporting, traceability, and a single source of truth for all testing activities.
Look for solutions that seamlessly support both manual and automated testing workflows, enabling teams to maintain unified visibility across all testing activities. Deep integration with development tools like Jira and GitHub is essential, ensuring that testing remains intrinsically connected to broader project management processes and team collaboration.
Measuring CI/CD Test Automation Success
Key Performance Indicators to Track
Establish metrics that demonstrate the value of your test automation investment. Common indicators include reduction in manual testing effort, decreased time from code commit to deployment, improved defect detection rates, and increased deployment frequency.
Track both leading indicators (test coverage, execution time) and lagging indicators (production defects, customer satisfaction) to understand the full impact of your automation program. Regular measurement helps identify areas for optimization and justifies continued investment.
Continuous Improvement Processes
Implement regular retrospectives to evaluate automation effectiveness and identify improvement opportunities. Gather feedback from developers, testers, and operations teams about pain points and suggestions for enhancement.
Use data-driven approaches to optimize test selection, execution strategies, and maintenance processes. Automation should evolve continuously to support changing application requirements and development practices.
The Future of Test Automation in CI/CD
What Emerging Trends Should You Watch?
Artificial intelligence is transforming test automation with capabilities like intelligent test generation, self-healing tests, and predictive failure analysis. AI testing adoption has increased from 7% in 2023 to 16% in 2025, indicating growing interest in these advanced capabilities.
Low-code and no-code testing platforms are democratizing automation by enabling non-technical team members to contribute to test creation and maintenance. This trend expands testing capability while reducing the bottleneck of specialized automation skills.
Preparing for Evolving Requirements
Modern applications increasingly involve cloud-native architectures, microservices, and complex integration patterns that challenge traditional testing approaches. Prepare your automation strategy to handle distributed systems, API-first architectures, and dynamic infrastructure.
Consider how emerging technologies like containers, serverless computing, and edge deployment affect your testing requirements. Automation strategies must evolve to address these architectural changes while maintaining effectiveness and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What percentage of testing should be automated in a CI/CD pipeline? Organizations using test automation report significant improvements in application quality, with teams typically focusing automation on regression testing and repetitive scenarios while maintaining manual testing for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc scenarios. The exact approach depends on your application complexity, team skills, and release frequency requirements.
How long should automated tests run in a CI/CD pipeline? Unit tests should complete in seconds, integration tests within minutes, and comprehensive end-to-end suites in under 30 minutes for optimal developer productivity. Use parallel execution and selective test running to optimize pipeline performance.
What's the biggest challenge when implementing test automation in CI/CD? Test maintenance overhead presents the greatest long-term challenge, requiring ongoing effort to update tests as applications evolve. Address this through proper test design, coding standards, and regular maintenance cycles. A robust test management platform can aid in enforcing these standards and streamlining maintenance efforts.
Which tools are essential for CI/CD test automation? Essential tools include a CI/CD platform (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions), automation frameworks tailored to your technology stack, test data management solutions, and comprehensive reporting capabilities. A unified test management platform, like TestQuality, bridges manual and automated testing, integrating seamlessly with your development ecosystem to provide a single source for all quality data.
How do you handle flaky tests in automated CI/CD pipelines? Address flaky tests immediately through improved wait strategies, better test isolation, stable test environments, and robust error handling. Never ignore flaky tests—they undermine confidence in your entire automation program.
Ready to Transform Your CI/CD Pipeline?
Implementing effective test automation in CI/CD pipelines requires strategic planning, the right tools, and ongoing commitment to continuous improvement. Success comes from starting with clear objectives, choosing appropriate technologies, and building automation capabilities that scale with your development needs.
The investment in proper test automation pays dividends through faster delivery cycles, improved software quality, and increased team confidence in release processes. Teams that master these practices gain significant competitive advantages in their ability to respond to market demands and customer feedback.
TestQuality provides the unified test management platform that bridges manual and automated testing within your CI/CD workflows. With seamless integrations for GitHub, Jira, and popular automation frameworks, TestQuality enables teams to achieve their quality goals while maintaining development velocity. Start your free trial today and discover how unified test management transforms your automation strategy.