AI testing limitations are real and well-documented, making human-in-the-loop QA essential for delivering quality software in 2026 and beyond.
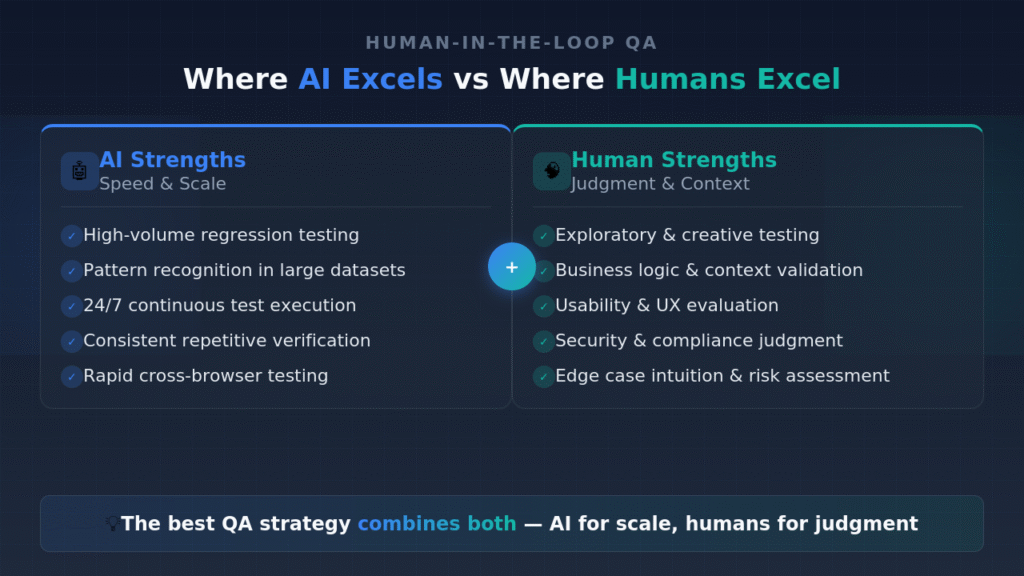
- AI excels at pattern recognition and repetitive test execution but fails at understanding context, user intent, and business-critical nuances that determine true software quality.
- Risk-based testing helps teams allocate human expertise where it matters most while letting AI handle high-volume, low-complexity verification tasks.
- Organizations that implement hybrid testing approaches report stronger defect detection rates and fewer production incidents than those relying on AI alone.
- The future of QA belongs to teams that treat AI as an amplifier of human expertise rather than a replacement for critical thinking.
Balance your automation investments with human oversight to avoid the costly AI failures that have plagued organizations rushing toward full autonomy.
The AI hype train has been running at full speed through the software testing industry. Every vendor promises autonomous testing, self-healing scripts, and QA teams that can finally take that vacation. What the marketing materials conveniently omit is this: Stanford's AI Index documented 233 AI incidents in 2024, a 56% increase from the previous year. Many of these failures occurred in systems that stakeholders believed were bulletproof.
AI testing limitations are production incidents waiting to happen. The organizations seeing real ROI from AI in their test management workflows understand exactly where AI falls short and deploy human expertise to fill those gaps.

What Are the Real AI Testing Limitations QA Teams Face?
The conversation around AI in testing often focuses on what these tools can do. The more important question is what they consistently fail to do well. Understanding these limitations is a smart way to look at your testing investments.
The Context Problem
AI models operate on statistical correlations. They identify patterns in training data and apply those patterns to new situations. This logic works brilliantly for structured, repetitive tasks. It fails spectacularly when context matters.
Consider a payment processing flow that works correctly from a functional standpoint but exposes sensitive data in browser developer tools. An AI testing tool will verify that transactions complete successfully. It lacks the contextual awareness to recognize that displaying unmasked credit card numbers violates PCI compliance, even if the feature "passes" every functional test.
Human testers bring domain knowledge, regulatory awareness, and an understanding of user expectations that current AI systems can't replicate. They ask questions like "Should this happen?" rather than just "Did this happen?" These critical thinking skills are beyond AI's reach.

The Black Box Dilemma
Modern AI testing tools generate test cases, predict failure points, and self-heal broken scripts. What they can't do is explain their reasoning in ways that support debugging and continuous improvement.
When an AI-generated test fails, QA teams often face a frustrating reality: they know something broke, but they don't know why the AI tested that particular scenario or what business logic the test was meant to validate. This opacity creates a knowledge gap that compounds over time. Teams become dependent on tools they don't fully understand and testing scenarios they didn't consciously choose to prioritize.
Gartner predicts that by 2028, 90% of enterprise software engineers will use AI code assistants, shifting their role from implementation to orchestration. But orchestration requires understanding, and understanding requires transparency that current AI testing tools rarely provide.
The Edge Case Blindness
AI models learn from existing data. They become excellent at identifying patterns similar to what they've seen before. Edge cases, by definition, are scenarios that don't fit established patterns.
A financial application handling currency conversions might be thoroughly tested by AI across common currency pairs. But what happens when a user selects a currency that recently experienced a dramatic exchange rate shift due to geopolitical events? The AI has no mechanism for recognizing that this scenario requires additional scrutiny because it falls outside historical norms.
When Does AI Fail in Testing Scenarios?
Recognizing when AI fails testing helps teams deploy human expertise where it delivers the highest impact. Certain testing scenarios consistently expose AI limitations.
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing thrives on creativity, intuition, and the ability to follow unexpected threads. Testers pursue hunches, combine features in unusual ways, and probe boundaries that requirements documents never anticipated.
AI lacks curiosity. It can't wonder what might happen if a user interrupts a workflow midway, returns to it hours later, and attempts to resume from a stale state. Human testers pursue these scenarios because experience tells them such edge cases often reveal serious defects. Effective exploratory test management bridges structured testing with the creative investigation that catches the bugs automated scripts miss.
Usability and User Experience
An interface can be functionally correct while being practically unusable. AI testing tools verify that buttons respond to clicks, forms accept input, and navigation links lead to expected destinations. They can't evaluate whether the user experience makes sense.
Does the error message help users understand what went wrong? Is the information hierarchy logical? Will first-time users find the workflow intuitive? These questions require human judgment informed by empathy for end users. AI perceives structure but not experience.
Security and Compliance Validation
Security testing demands adversarial thinking. Skilled security testers imagine how malicious actors might abuse legitimate features, bypass controls, or exploit assumptions in system design. AI tools can run predetermined security scans, but they can't think like attackers.
Compliance validation presents similar challenges. Regulations evolve. Industry interpretations shift. What constituted compliant behavior last quarter might violate new guidance today. Human testers stay current with regulatory changes and understand the spirit behind requirements, enabling them to catch compliance issues that technically pass automated checks.
Business Logic Verification
Complex business rules create testing scenarios where correctness depends entirely on context. An insurance premium calculation might produce a mathematically accurate result that nonetheless violates business policies about risk categorization.
AI testing tools excel at verifying calculations match expected formulas. They can't evaluate whether those formulas appropriately implement business intent. This distinction matters enormously when software supports high-stakes decisions about finances, health, or safety.
How Does Human-in-the-Loop QA Improve Test Coverage?
Human-in-the-loop QA is about designing testing workflows that leverage AI capabilities while preserving human judgment where it matters most.
The Orchestration Model
In effective human-in-the-loop testing, AI handles volume while humans provide direction and validation. Automated tools execute thousands of regression tests nightly, flagging anomalies for human review. Rather than verifying every result manually, testers focus attention on unexpected outcomes and high-risk scenarios.
This orchestration model recognizes that human attention is a scarce resource in modern QA. AI extends the reach of that attention by filtering noise and surfacing signals that warrant investigation. Modern test automation strategies succeed when they amplify human capabilities rather than attempting to replace them entirely.

Checkpoint Validation
Effective human-in-the-loop implementations establish explicit checkpoints where human judgment is required before testing proceeds. AI-generated test cases might require human approval before entering the test suite. Automated test results might require human sign-off before influencing release decisions.
These checkpoints create accountability. Someone with domain expertise validates that AI recommendations align with business priorities and technical realities. When issues arise, the validation chain provides clear visibility into who approved what and why.
Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
Human-in-the-loop QA creates opportunities for AI systems to improve over time. When human testers reject AI recommendations or identify scenarios that automation missed, that feedback can inform future AI behavior.
Teams that establish structured feedback mechanisms see their AI tools become more valuable with each testing cycle. Teams that simply deploy AI without feedback find that their tools remain static while their applications evolve, creating growing gaps between what automation covers and what actually needs testing.
What Role Does Risk-Based Testing Play in Hybrid QA?
Risk-based testing provides a framework for deciding where human expertise delivers the most value. Rather than spreading human attention evenly across all testing activities, risk-based approaches concentrate effort on areas where failures would cause the greatest harm.
Prioritizing by Impact and Likelihood
Risk-based testing evaluates each system component based on two factors: the likelihood of failure and the impact if failure occurs. Components scoring high on both dimensions receive intensive human-led testing. Components with low risk scores become candidates for automated coverage.
| Risk Category | Likelihood | Impact | Testing Approach |
| Payment Processing | Medium | Critical | Human-led with AI support |
| User Authentication | Medium | Critical | Human-led with AI support |
| Core Business Logic | High | High | Human-led exploratory testing |
| Reporting Dashboard | Low | Medium | AI automation with spot checks |
| Static Content | Low | Low | Fully automated verification |
| Third-Party Integrations | High | High | Human validation of edge cases |
This matrix helps teams allocate limited human attention where it delivers maximum quality improvements. AI handles the high-volume, low-risk verification that would otherwise consume tester time without proportionate quality gains.

Adapting to Change
Static risk assessments become outdated as applications evolve. Features that were stable last quarter might become high-risk following significant refactoring. New functionality introduces unknown risk profiles that require investigation.
Effective risk-based testing programs include regular risk reassessment. Teams review historical defect data, analyze recent changes, and adjust testing priorities accordingly. This continuous calibration ensures human attention remains focused on areas of genuine concern rather than historical assumptions.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Risk-based testing fits naturally into continuous integration workflows. High-frequency automated tests provide rapid feedback on low-risk regressions. Human-led testing activities align with release gates where risk assessment informs go/no-go decisions.
A well-designed test automation strategy recognizes that different pipeline stages warrant different testing approaches. Unit tests might run with every commit. Integration tests might run on merge requests. Comprehensive human-led testing might be reserved for release candidates that have passed automated gates.
Five Scenarios Where AI Testing Falls Short
Identifying specific failure scenarios helps teams recognize when human oversight is essential.
- Regulatory compliance verification where requirements change frequently and interpretation matters as much as implementation. Human testers understand regulatory intent and catch violations that technically pass automated checks.
- Accessibility testing where user experience for people with disabilities requires evaluation beyond automated rule checking. WCAG compliance involves judgment calls about whether implementations meaningfully support accessibility.
- Localization validation where cultural appropriateness and linguistic nuance determine whether translations serve their intended audiences. AI can verify that strings are translated but can't evaluate whether translations convey appropriate meaning.
- Performance testing under realistic conditions where business scenarios drive load patterns that synthetic tests don't capture. Human testers design performance scenarios that reflect actual usage patterns and business priorities.
- Cross-system integration testing where failures emerge from interactions between components that each pass individual tests. Human testers understand system architecture and anticipate integration points where failures cluster.
How Do You Build an Effective Human-in-the-Loop Testing Program?
Implementing human-in-the-loop QA requires organizational commitment beyond selecting tools. Success depends on designing workflows, developing skills, and maintaining appropriate oversight.
Defining Clear Accountability
Hybrid testing models create ambiguity about responsibility. When AI-generated tests miss critical defects, who bears accountability? Clear governance frameworks establish expectations for human oversight and define consequences when oversight fails.
Organizations should document which decisions require human approval, who provides that approval, and what evidence supports approval decisions. This documentation serves both operational and compliance purposes, demonstrating appropriate oversight to auditors and stakeholders.
Developing Hybrid Skills
QA professionals working in human-in-the-loop environments need capabilities beyond traditional testing skills. They must understand AI tool limitations, critically interpret AI recommendations, and provide feedback that improves AI performance over time.
Training investments should address AI literacy, helping testers understand how their AI tools generate recommendations and where those recommendations commonly fail. Testers who understand AI mechanisms make better judgments about when to trust automation and when to investigate further.
Measuring What Matters
Traditional QA metrics like defect counts and test coverage percentages provide incomplete visibility into human-in-the-loop effectiveness. Additional metrics should capture the value human oversight provides.
Track scenarios where human judgment caught issues that automation missed. Measure the accuracy of AI recommendations and whether that accuracy improves over time with feedback. Evaluate whether human checkpoint reviews identify genuine concerns or merely add process overhead. These metrics demonstrate whether hybrid approaches deliver promised value.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can AI completely replace human testers in software QA?
No. AI excels at repetitive tasks and pattern recognition but lacks the contextual understanding, creativity, and business judgment that human testers provide. The industry consensus supports hybrid approaches where AI amplifies human capabilities rather than replacing them.
What is human-in-the-loop testing, and why does it matter?
Human-in-the-loop testing is a QA approach that combines AI automation with human oversight at strategic checkpoints. AI tools can miss context-dependent issues, compliance violations, and usability problems that human testers catch through experience and judgment. This hybrid model delivers better defect detection while maintaining the efficiency benefits of automation.
How do I know which tests should involve human oversight versus full automation?
Apply risk-based testing principles. Evaluate each system component based on failure likelihood and business impact. High-risk areas like payment processing, security features, and complex business logic warrant human-led testing. Low-risk areas like static content and stable utility functions can rely on automation with periodic human spot checks.
What skills do QA professionals need for human-in-the-loop testing?
QA professionals need traditional testing skills plus AI literacy. Understanding how AI tools generate recommendations helps testers critically evaluate those recommendations. Skills in providing effective feedback improve AI tool performance over time. Domain expertise remains essential for recognizing when AI suggestions miss important business context.
Transform Your Testing with Strategic Human Oversight
AI testing limitations are boundaries that define where human expertise creates irreplaceable value. Teams that recognize these boundaries and design testing programs around them consistently outperform teams chasing full automation.
The path forward combines AI efficiency with human insight. Let automation handle the tasks it does well: high-volume regression verification, pattern detection across large datasets, and continuous monitoring of production systems. Reserve human attention for the work that truly requires it: exploratory testing, business logic validation, compliance verification, and the judgment calls that determine whether software actually serves its users.
TestQuality provides a unified test management platform that supports both manual and automated testing workflows, enabling teams to implement effective human-in-the-loop QA strategies. Start your free trial and discover how integrated test management helps you balance AI capabilities with the human expertise your quality depends on.