Key Takeaways
Exploratory testing uncovers hidden defects that scripted tests miss through real-time, adaptive investigation.
- Widely adopted across organizations, leveraging tester expertise to discover complex, multi-interaction bugs that automated scripts overlook
- Best suited for early development stages, agile environments, and new feature validation where requirements evolve rapidly and flexibility matters most
- Combines with automation for comprehensive coverage, using test charters and session-based management to balance structure with creative investigation
- Requires skilled testers and modern test management platforms to document findings effectively while maintaining the spontaneity that makes this approach valuable
The software testing market is experiencing explosive growth, projected to reach $145.84 billion by 2037 as organizations prioritize quality assurance. Within this landscape, exploratory testing has emerged as an essential technique that complements traditional QA methods. Unlike scripted tests that follow predetermined paths, exploratory testing empowers testers to investigate software dynamically, discovering issues that automated checks and rigid test cases frequently miss.

Research demonstrates that exploratory testing excels at catching complex defects requiring multiple user interactions. While test case-based testing handles immediately visible issues effectively, exploratory approaches uncover the subtle, multi-step failures that frustrate real users. This testing type represents a critical capability for teams navigating fast-paced development cycles where requirements shift constantly and comprehensive test coverage demands both structure and spontaneity.
What is Exploratory Testing?
Exploratory testing is a dynamic approach where test design and execution happen simultaneously. Rather than following predefined scripts, testers actively investigate the application, making real-time decisions about what to test based on their observations and domain knowledge. This method emphasizes learning, adaptation, and creativity.
The approach differs fundamentally from scripted testing. Where traditional tests verify known behaviors against documented requirements, exploratory testing seeks unknown issues through intuition and experience. According to the Ministry of Testing, testers start with broad objectives like "investigate login functionality" and navigate the software organically, adjusting their strategy as they discover new information.
Consider testing a new e-commerce checkout process. A scripted test might verify that clicking "Place Order" creates a database entry. An exploratory test session could reveal that rapidly switching between payment methods causes session data corruption, or that using browser back buttons at specific points creates duplicate charges. These are the edge cases and unexpected behaviors that formal test cases often miss because nobody anticipated them during test planning.
This testing style traces back to Cem Kaner's 1984 formalization, though testers had practiced similar techniques informally for years. Today, it represents a core component of modern testing strategies, particularly within agile methodologies where software testing effectiveness depends on rapid feedback and continuous adaptation.

What Are the Key Benefits of Exploratory Testing?
Organizations implement exploratory testing because it delivers distinct advantages that scripted approaches cannot match. Understanding these benefits helps teams allocate testing resources strategically.
5 Compelling Reasons to Practice Exploratory Testing
1. Discovers Hidden Edge Cases
Exploratory testing uncovers unusual scenarios that test scripts overlook. Testers follow their intuition into unexpected application areas, revealing defects in rarely-traveled code paths. The software testing industry increasingly recognizes this approach as essential for finding bugs that automation cannot detect. These are the issues that appear only when users deviate from "happy path" workflows.
2. Adapts to Changing Requirements
Agile environments demand flexibility. Requirements evolve weekly, making comprehensive test script maintenance impractical. Exploratory testing thrives in this uncertainty. Testers adjust their investigation focus as new features emerge or priorities shift, providing valuable feedback without waiting for formal test case updates.
3. Accelerates Feedback Loops
Speed matters in continuous integration environments. Exploratory testing delivers rapid insights without extensive preparation. Testers can begin investigating new builds immediately, identifying critical issues within hours rather than days. This quick feedback helps development teams address problems before they propagate through the codebase.
4. Validates User Experience Authentically
Scripts verify functionality exists. Exploratory testing evaluates whether features work intuitively. Testers approach software as real users would, identifying confusing workflows, misleading labels, and frustrating interactions. This user-centric perspective reveals usability problems that technical validation misses entirely.
5. Complements Automation Strategically
Rather than replacing automated testing, exploratory work enhances it. Insights gained through investigation inform which scenarios deserve automation. Testers discover the high-value test cases worth scripting for regression coverage while automation handles repetitive validation. This combination maximizes both efficiency and coverage depth.
Industry research comparing testing methodologies demonstrates that exploratory approaches excel at finding complex defects that require multiple steps to trigger. While automated tests catch immediate failures, exploratory testing reveals issues requiring specific sequences of user inputs and particular timing conditions. The software quality assurance market increasingly recognizes this complementary relationship, with modern frameworks designed to support both scripted and exploratory approaches.

When Should You Use Exploratory Testing?
Knowing when exploratory testing delivers maximum value helps teams deploy resources effectively. Certain situations particularly benefit from this adaptive approach.
Early Development Stages
When code changes rapidly and requirements remain fluid, exploratory testing provides essential feedback without rigid test maintenance. Testers can evaluate evolving features immediately, identifying fundamental issues before they become architectural problems. This early discovery reduces costly rework later in the development cycle.
Agile and DevOps Environments
Fast-paced methodologies demand testing flexibility. Sprint cycles compress timelines, making comprehensive script updates impractical between iterations. Exploratory testing adapts naturally to these constraints, allowing teams to maintain quality without testing bottlenecks. The approach aligns perfectly with behavior-driven development principles that emphasize collaboration and rapid iteration.
New Feature Validation
Introducing functionality into existing systems creates integration risks. Exploratory testing reveals unexpected interactions between new and legacy code. Testers investigate how features behave within the broader application context, discovering issues that isolated unit tests miss.
User Acceptance Testing Phases
UAT benefits tremendously from exploratory approaches. Stakeholders interact with software naturally rather than following scripts, mimicking actual usage patterns. This authentic interaction surfaces usability problems and workflow confusions that formal test cases don't address.
Complementing Automated Test Suites
Even comprehensive automation leaves gaps. Exploratory testing fills these spaces by investigating areas automation doesn't reach. It also validates that automated tests remain relevant as applications evolve.
The table below clarifies when each testing approach delivers optimal results:
| Scenario | Best Approach | Reasoning |
| Regression validation for stable features | Scripted/Automated | Repetitive checks benefit from automation efficiency |
| Investigating new functionality | Exploratory | Unknown behaviors require adaptive investigation |
| Compliance requirement verification | Scripted | Regulatory needs demand documented, repeatable tests |
| Usability and UX evaluation | Exploratory | Human judgment assesses user experience authentically |
| Performance baseline monitoring | Automated | Consistent metrics require standardized measurement |
| Complex user workflow validation | Exploratory | Multi-step scenarios reveal integration issues |
| Security vulnerability discovery | Combined | Automated scans plus exploratory probing maximize coverage |
Organizations achieve best results by strategically combining exploratory work with automated testing and formal test cases. Each approach addresses different quality aspects, creating comprehensive coverage when deployed thoughtfully.
How Do You Perform Exploratory Testing Effectively?
While exploratory testing emphasizes freedom and creativity, structure ensures productive sessions that deliver actionable insights. Several proven techniques help teams practice this approach effectively.
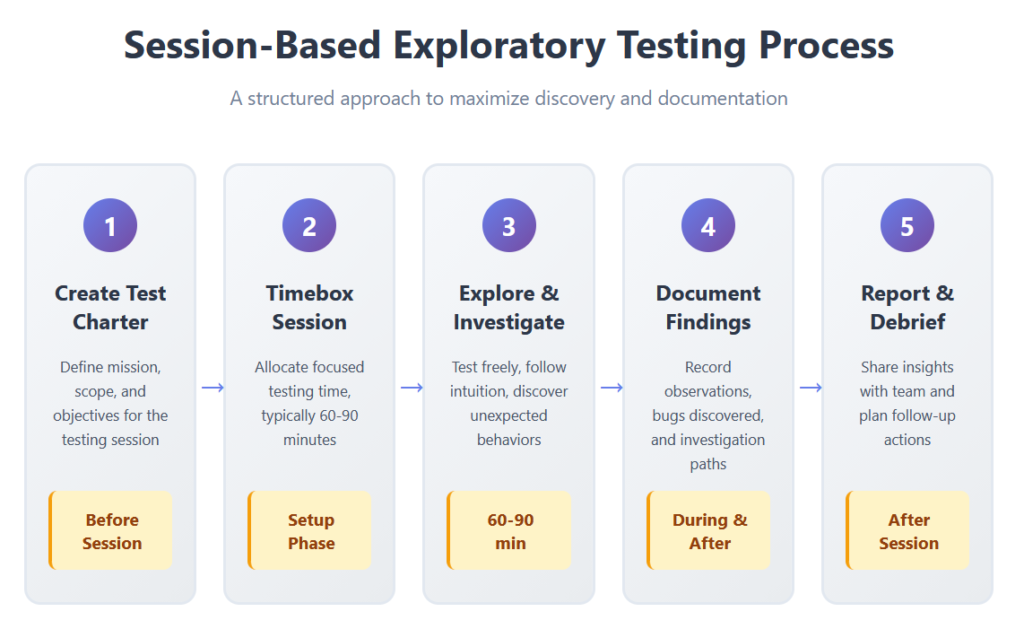
Develop Clear Test Charters
Test charters provide focus without rigid constraints. These brief mission statements outline session objectives like "explore payment processing with various card types" or "investigate mobile responsiveness across authentication flows." Charters keep testing targeted while allowing creative investigation. They typically specify the feature area, testing goal, and any particular risks to investigate.
Well-crafted charters balance specificity with flexibility. They define what to test without prescribing how to test it. This structure helps testers maintain productivity while exercising professional judgment about which paths warrant deeper exploration.
Implement Timeboxing Practices
Session-based test management uses timeboxing to maintain focus and measure effort. Teams allocate specific durations for testing sessions, typically 60 to 90 minutes. This constraint prevents fatigue and creates natural break points for documenting findings.
Timeboxing also enables better resource planning. Managers can estimate testing capacity and adjust session durations based on complexity. If critical issues emerge, teams can extend sessions by 30-45 minutes, but defined endpoints prevent endless investigation that yields diminishing returns.
Practice Collaborative Testing
Pair testing enhances exploratory effectiveness. Two testers working together bring diverse perspectives and catch issues individual testers might miss. One person can navigate the application while the other documents observations, or both can alternate roles throughout the session.
This collaboration also facilitates knowledge transfer. Junior testers learn investigation techniques from experienced colleagues, while fresh eyes often spot patterns that veterans overlook through familiarity.
Document Sessions Systematically
Despite its informal nature, exploratory testing requires documentation. Teams should record their investigation paths, unexpected behaviors, and defects discovered. Session notes capture valuable context that helps developers reproduce issues and prevents duplicate testing effort.
Modern approaches use screen recording tools, detailed logs, and structured session reports. These artifacts serve multiple purposes: bug reproduction, test coverage tracking, and identifying areas requiring additional investigation. Effective documentation transforms exploratory work from ad hoc activity into a managed process that contributes to organizational knowledge.
Combine with Automation and Scripted Tests
The most effective testing strategies integrate multiple approaches. Teams use exploratory testing to discover new test scenarios, then automate high-value cases for regression coverage. This workflow ensures that creative investigation informs automated test development rather than automation replacing exploration entirely.
Organizations practicing shift-left testing incorporate exploratory work early in development cycles. Testers investigate features as code becomes available, providing rapid feedback that prevents defects from propagating. This early engagement maximizes the value of both exploratory and automated testing approaches.
What Tools Support Exploratory Testing Best?
While exploratory testing emphasizes human judgment over tooling, several platforms significantly enhance effectiveness. The right tools balance documentation requirements with the spontaneity that makes this approach valuable.
Test Management Platforms
Comprehensive test management systems help teams organize exploratory sessions, track findings, and maintain coverage visibility. These platforms allow testers to create session plans, document observations in real time, and link discovered defects to specific investigation areas.
Modern test management tools integrate with development workflows, automatically capturing test execution data within broader quality metrics. This integration ensures exploratory work receives appropriate visibility alongside automated test results and formal test case execution.
Session Recording Solutions
Screen recording tools capture tester interactions during exploratory sessions. These recordings serve as invaluable artifacts for reproducing defects and understanding exactly how issues were discovered. Developers can replay sessions to see the precise steps that triggered problems, eliminating the ambiguity that often accompanies verbal bug descriptions.
Recording tools also facilitate knowledge sharing. Team members can review sessions to understand investigation techniques and learn about application behaviors they haven't personally explored.
Collaboration and Communication Platforms
Real-time collaboration tools enable distributed teams to conduct pair testing sessions remotely. Video conferencing, shared screen access, and instant messaging support the interactive nature of exploratory work across geographic boundaries.
These platforms also streamline communication between testers and developers. Quick feedback loops accelerate defect resolution, particularly when teams can discuss issues immediately during investigation rather than waiting for formal bug report processing.
Unified Test Management with TestQuality
Organizations seeking comprehensive testing solutions benefit from platforms that support multiple testing approaches within a single system. This unified approach ensures exploratory testing insights integrate seamlessly with automated test results, manual test cases, and requirements traceability.
A robust test management platform provides the structure needed for productive exploratory work without constraining the creative investigation that makes this approach effective. Teams can plan sessions, document findings, and analyze coverage while maintaining the flexibility that distinguishes exploratory testing from rigid scripted approaches. Integration with development tools like GitHub and Jira ensures exploratory discoveries contribute to the complete quality picture.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does exploratory testing differ from ad hoc testing?
While both lack predefined scripts, exploratory testing follows structured approaches like session-based test management with clear charters and documentation requirements. Ad hoc testing typically involves less planning and may not capture systematic findings. Exploratory work balances freedom with accountability through defined sessions and recorded outcomes.
Can exploratory testing work effectively in regulated industries?
Yes, when properly documented. Regulatory environments require evidence of testing thoroughness. Organizations use session-based test management to create audit trails showing what was tested, by whom, and with what results. Test charters and session reports provide the documentation needed for compliance while maintaining investigative flexibility.
Should junior testers perform exploratory testing?
Junior testers can participate effectively, especially in pair testing scenarios where they learn from experienced colleagues. However, exploratory testing generally benefits from domain knowledge and testing expertise. Organizations often have senior testers conduct initial exploratory work on complex features, then involve junior team members in follow-up sessions.
How do you measure exploratory testing coverage?
Coverage metrics for exploratory testing focus on features investigated rather than test cases executed. Teams track which application areas received attention during sessions, time invested per feature, and defect discovery rates. Session reports documenting investigation paths provide visibility into testing thoroughness without requiring predefined test case counts.
Transform Your Testing Strategy with Exploratory Testing
The software quality assurance market continues expanding as organizations recognize that comprehensive testing requires diverse approaches. Exploratory testing delivers unique value by combining human creativity with systematic investigation, uncovering the complex issues that scripts and automation frequently miss.
Successful quality assurance strategies balance structure with flexibility. Exploratory testing provides the adaptability modern development demands while complementing automated coverage and formal test cases. Teams that implement this approach effectively discover more defects, deliver better user experiences, and respond more rapidly to changing requirements.
TestQuality provides a modern, unified test management platform that supports all testing types within development workflows. With seamless integration for both manual and automated testing, TestQuality empowers teams to implement exploratory testing alongside comprehensive QA approaches. Ready to enhance your testing strategy? Start your free trial today and discover how unified test management transforms quality assurance.