Key Takeaways
Gherkin automated testing bridges the gap between business requirements and technical implementation while future-proofing your test automation strategy.
- Team alignment improves dramatically when QA, developers, and stakeholders collaborate using plain-language Gherkin scripts
- Maintenance costs drop significantly as declarative scenarios resist UI changes and implementation shifts
- AI integration accelerates test generation and execution when combined with modern Gherkin automation frameworks
- Living documentation automatically generated, as Gherkin tests serve dual purposes throughout the development lifecycle, keeping specifications in sync with actual application behavior.
The verdict: Teams adopting gherkin automated testing in 2026 gain competitive advantages through faster releases, clearer communication, and more resilient test suites.
The test automation landscape has shifted dramatically. Teams releasing software multiple times per week need testing strategies that keep pace without breaking under constant change. According to MarketsandMarkets research, the global automation testing market is projected to reach $55.2 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual rate of 14.5%, with behavior-driven development approaches becoming central to this transformation.
Enter gherkin automated testing, where human-readable specifications meet executable test automation. This approach has become essential for development teams navigating rapid release cycles while maintaining software quality. The question isn't whether to adopt Gherkin for test automation, but rather how quickly your team can implement it effectively.

What Is Gherkin Automated Testing?
Gherkin automated testing combines behavior-driven development methodology with executable specifications. At its core, Gherkin is a domain-specific language that structures test scenarios using simple keywords: Given, When, and Then. These keywords create a framework that both humans and automation tools understand.
The magic happens when these readable specifications connect directly to automation frameworks like Cucumber, SpecFlow, or Behave. Teams write scenarios describing expected software behavior in plain English, then map these scenarios to automated test code. This creates a powerful bridge between business requirements and technical validation.
Unlike traditional test automation that requires deep programming knowledge, gherkin automation allows anyone on your team to understand what's being tested and why. A QA engineer, product manager, and developer can all read the same Gherkin scenario and grasp its intent immediately. This shared understanding eliminates the translation gaps that plague many testing initiatives.
The structure follows a consistent pattern. The Given step establishes preconditions, the When step describes the action being tested, and the Then step verifies the expected outcome. Additional keywords like And and But allow for complex scenarios without sacrificing readability. This simplicity makes Gherkin scripts maintainable over time, even as team members change and applications evolve.
Why Are Teams Choosing Gherkin Automation in 2026?
The adoption of gherkin automated testing continues accelerating because it solves real problems that development teams face daily. Here are the compelling reasons driving this growth.
1. Cross-Functional Collaboration Actually Works
Teams implementing Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) testing report dramatically improved communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders. Product owners contribute directly to test scenarios without learning programming languages. Developers gain clarity about business expectations before writing code. QA teams validate requirements early in the development cycle rather than discovering misunderstandings during execution.
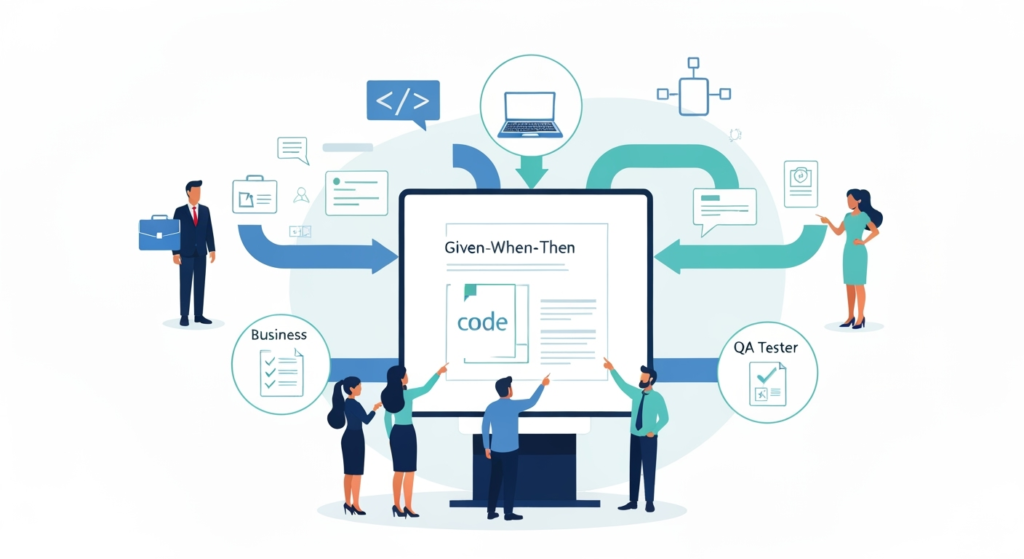
Visualizing the BDD Workflow: Bridging Business and Code with Gherkin.
This collaboration reduces expensive rework. When everyone agrees on expected behavior upfront through Gherkin scripts, fewer surprises emerge during testing phases. The shared language creates alignment that traditional requirement documents rarely achieve.
2. Test Maintenance Becomes Manageable
Traditional automated tests break frequently when UI elements change. Gherkin automation resists this brittleness through declarative scenario writing. Instead of specifying that a user clicks button ID "submit-btn-123," Gherkin scripts describe the user submitting a form. When developers refactor the interface, the underlying step definitions update while scenarios remain untouched.
This separation of concerns pays enormous dividends as applications mature. Teams report spending less time fixing broken tests and more time expanding test coverage. The abstraction layer that Gherkin provides protects test investments from implementation churn.
3. Living Documentation Emerges Automatically
Gherkin scenarios serve dual purposes: as executable tests and as up-to-date documentation. Unlike traditional documentation, which often goes stale quickly, Gherkin tests that fail immediately alert teams to documentation inaccuracy immediately. This self-correcting system ensures documentation stays synchronized with actual application behavior.
New team members onboarding can read through feature files to understand system capabilities. Support teams reference scenarios when investigating customer issues. Product managers use them to track feature completeness. This multi-purpose utility makes the time invested in writing quality Gherkin scripts pay returns across the entire organization.
4. AI and Automation Amplify Gherkin's Power
Modern AI tools are beginning to transform how teams create and maintain gherkin automated testing. The natural language structure of Gherkin makes it ideal for AI interpretation. Machine learning models trained on test scenarios can suggest test cases, identify gaps in coverage, and even generate step definitions. This AI augmentation allows small teams to achieve test coverage that previously required much larger QA departments.

Early adopters are leveraging AI-powered test generation tools that analyze application requirements to produce Gherkin scenarios. These tools, while continuously evolving, represent a significant shift toward more intelligent test automation that leverages the human-readable format of Gherkin scripts.
5. Framework Flexibility Supports Any Tech Stack
Gherkin automation isn't tied to specific programming languages or frameworks. Teams working in Java use Cucumber. .NET teams implement SpecFlow. Python developers leverage Behave. This flexibility means organizations can standardize on Gherkin syntax while maintaining their preferred technology stacks.
The ecosystem continues expanding with better integrations. Modern test management platforms like TestQuality natively support importing Gherkin feature files, connecting them seamlessly with GitHub workflows and Jira requirements. Teams can maintain Gherkin scripts in version control alongside application code while managing execution through specialized test platforms.
6. Shift-Left Testing Becomes Natural
Gherkin encourages teams to define expected behavior before implementation begins. This shift-left approach catches issues when they're cheapest to fix during the design and development phases rather than during testing or production. Writing Gherkin scenarios during planning sessions forces conversations about edge cases and error conditions that teams might otherwise overlook.
The Ministry of Testing community emphasizes this benefit in their BDD resources. Teams practicing BDD report finding defects earlier in the development cycle, reducing the downstream costs of quality issues. The collaborative scenario writing process itself reveals ambiguities and contradictions in requirements before any code gets written.
7. Regression Testing Becomes Comprehensive Yet Targeted
As test suites grow, running every test for every change becomes impractical. Gherkin's tagging system allows teams to categorize scenarios and run specific subsets intelligently. Critical path tests run on every commit. Comprehensive regression suites run nightly. Feature-specific tests execute only when relevant code changes.
This intelligent test selection keeps feedback loops fast while maintaining thorough coverage. Teams avoid the trap of either running insufficient tests or waiting hours for massive test suites to complete. The balance between speed and coverage that Gherkin automation enables supports modern continuous delivery practices.
How Does Gherkin Automation Work?
Understanding the technical flow helps teams implement gherkin automated testing successfully. The process moves through distinct phases from scenario creation to test execution.
Writing effective Gherkin starts with identifying the feature being tested. Feature files organize related scenarios and provide context. Each feature contains one or more scenarios describing specific behaviors. These scenarios follow the Given-When-Then structure to establish context, describe actions, and verify outcomes.
Step definitions form the technical bridge between readable Gherkin and executable code. When automation frameworks like Cucumber encounter a Gherkin step, they search for matching step definitions. These step definitions contain the actual code that interacts with the application under test. A single step definition can support multiple scenarios, promoting code reuse and maintainability.
The execution engine reads feature files, matches steps to definitions, and runs the associated code. Results flow back through the framework, marking each step and scenario as passed or failed. Modern frameworks generate detailed reports showing which scenarios succeeded, which failed, and why. These reports integrate with CI/CD pipelines, providing immediate feedback on test status.
Parameterization adds power through scenario outlines. Rather than writing separate scenarios for similar test cases with different data, teams create templates. These templates execute multiple times with different values from an examples table. This data-driven approach expands test coverage without multiplying scenario maintenance.
Background sections reduce repetition by defining steps common to all scenarios in a feature. These shared setup steps run before each scenario, establishing consistent starting states. This keeps individual scenarios focused on their unique aspects while maintaining the necessary context.
Seamless integration with modern test management platforms completes the automation cycle. Platforms designed for BDD, such as TestQuality, import Gherkin feature files directly, linking them to requirements in Jira or user stories in GitHub. Test execution results then flow back automatically, providing comprehensive traceability from initial requirements through implementation to final validation.

What Are the Best Practices for Gherkin Scripts?
Writing effective Gherkin automation requires discipline and adherence to best practices that support long-term maintainability. Adopting these patterns is crucial for successful implementation and avoiding common pitfalls.
Focus scenarios on behavior rather than implementation details. Describe what the system should do from a user perspective, not how it accomplishes the task. For example, "When the customer completes checkout" communicates intent better than "When the customer clicks the submit button and enters payment information in the modal dialog." The former remains valid even if the UI changes completely.
Keep scenarios independent and executable in any order. Each scenario should set up its own preconditions rather than depending on previous scenarios. This independence allows running subsets of tests without worrying about execution sequence. It also makes debugging failures simpler since each scenario stands alone.
Use declarative language that abstracts away UI details. Instead of imperative steps like "I navigate to the login page, I enter my username in the username field, I enter my password in the password field, I click the login button," write declaratively: "I log in as a registered customer." This abstraction makes tests resilient to UI changes and easier to read.
Limit scenario length to maintain readability. Scenarios stretching beyond seven or eight steps often indicate opportunities to split functionality or abstract repeated patterns into background sections. Shorter scenarios are easier to understand, debug, and maintain. They also tend to test more focused behaviors, improving test granularity.
Choose meaningful names for scenarios that describe the behavior being tested. "Successful login with valid credentials" conveys more than "Login test 1." Good names serve as documentation, making feature files scannable references for understanding system behavior.
Implement proper tagging strategies from the start. Tags organize scenarios by feature area, test type, criticality level, or execution requirements. Consistent tagging enables intelligent test selection as suites grow. Common tag patterns include @smoke for critical path tests, @regression for comprehensive coverage, and feature-specific tags for targeted execution.
Maintain step definition reusability across scenarios. Well-written step definitions serve multiple scenarios, reducing code duplication. When creating new step definitions, check whether existing ones can be parameterized to handle the new case. This discipline keeps step definition files manageable as test suites expand.
How Do You Integrate Gherkin With Modern Test Automation Tools?
The ecosystem supporting gherkin automated testing has matured significantly, offering robust integration options for modern development workflows. Understanding these integrations helps teams maximize their automation investments.
Cucumber remains the most widely adopted Gherkin framework, supporting multiple programming languages including Java, JavaScript, Ruby, and Kotlin. Its extensive plugin ecosystem connects to testing libraries like Selenium for web automation, Appium for mobile testing, and REST Assured for API validation. Teams can leverage existing technical expertise while adopting gherkin automation practices.
SpecFlow serves .NET teams with deep Visual Studio integration and native C# support. It follows the same Gherkin syntax as Cucumber but optimizes for Microsoft technology stacks. SpecFlow's living documentation features generate readable specifications from test execution, creating up-to-date reference materials automatically.
Behave brings Gherkin to Python environments with Pythonic step definition patterns. Its integration with Python testing frameworks makes it natural for teams already invested in Python tooling. The framework's emphasis on clear error messages helps developers quickly identify and fix test failures.
Modern platforms like TestQuality elevate Gherkin beyond individual frameworks by providing unified test management across manual and automated testing. These platforms import Gherkin feature files, link scenarios to requirements, and aggregate results from multiple automation frameworks. The integration creates comprehensive visibility into testing status while maintaining the flexibility to use different automation tools for different test types.
CI/CD pipeline integration ensures gherkin automated testing provides continuous feedback. Tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, CircleCI, and GitLab CI/CD all support executing Gherkin tests as part of automated build processes. Results feed back into development workflows, blocking merges when critical scenarios fail or providing deployment confidence when comprehensive test suites pass.
The integration between test automation frameworks and test management platforms represents a significant maturity milestone. Teams no longer choose between framework flexibility and management visibility. Modern integrations provide both, allowing technical teams to optimize their automation approaches while giving stakeholders clear insights into quality status.
What Challenges Should You Expect With Gherkin Automation?
Implementing Gherkin automated testing, while highly beneficial, introduces challenges that teams must navigate thoughtfully. Acknowledging these obstacles upfront helps organizations plan realistic and successful adoption strategies.
The learning curve requires investment. While Gherkin syntax itself is simple, writing effective scenarios that remain maintainable over time requires practice. Teams need training on BDD principles, scenario design patterns, and the distinction between declarative and imperative writing styles. Organizations should budget time for this learning process rather than expecting immediate proficiency.
Step definition management becomes complex as test suites grow. Without discipline, teams accumulate duplicate step definitions with slight variations, creating maintenance nightmares. Establishing naming conventions, regular refactoring sessions, and code review practices for step definitions prevents this proliferation. Some teams assign step definition ownership to specific developers who ensure consistency. An unified test management platform can greatly assist in tracking and managing step definition ownership and reusability.
Stakeholder engagement requires sustained effort. The collaboration benefits of gherkin automation only materialize when non-technical stakeholders actively participate in scenario creation and review. This requires cultural change in many organizations. Product owners and business analysts need to see the value of investing time in scenario development rather than delegating it entirely to QA teams.
Test execution time can grow significantly as Gherkin test suites expand. Comprehensive scenario coverage combined with end-to-end test execution creates lengthy test runs. Teams address this through intelligent test selection using tags, parallel execution across multiple environments, and hybrid approaches that combine unit testing for speed with strategic Gherkin scenarios for integration validation.
The abstraction that makes Gherkin scenarios maintainable can also hide important details from test failures. When a scenario fails, determining the root cause sometimes requires diving into step definition code. Well-structured logging, clear error messages from step definitions, and integration with debugging tools help teams diagnose failures efficiently.
False confidence can emerge when teams focus heavily on Gherkin scenarios while neglecting other testing types. Gherkin automated testing excels at validating user-facing behavior but shouldn't replace unit testing, performance testing, or security testing. A balanced testing strategy uses Gherkin for BDD scenarios while maintaining appropriate coverage at other testing levels.
What Does the Future Hold for Gherkin Automated Testing?
The trajectory of gherkin automation points toward deeper AI integration, broader tooling support, and tighter alignment with modern development practices. Several trends are reshaping how teams approach BDD testing.
AI-powered test generation is transitioning from experimental to practical. Machine learning models trained on repositories of Gherkin scenarios can suggest relevant test cases based on requirement documents or user stories. These AI assistants help teams achieve more comprehensive coverage faster while maintaining the human oversight necessary for quality scenarios.
Self-healing tests represent the next evolution in test resilience. AI systems can detect when application changes break step definitions and suggest fixes. This addresses one of gherkin automation's persistent challenges by reducing the maintenance burden when UI elements change or API contracts evolve.
No-code platforms are democratizing test automation further by providing visual interfaces for creating Gherkin scenarios and step definitions. These tools allow business analysts and product owners to contribute directly to test automation without programming skills. The underlying automation still uses traditional frameworks, but the abstraction layer removes technical barriers to participation.
Visual AI testing combined with Gherkin scenarios creates powerful validation capabilities. Instead of fragile element locators, tests can verify expected layouts and designs using AI-powered image recognition. Gherkin scenarios describe expected visual outcomes in natural language while AI handles the technical complexity of visual validation.
Integration ecosystems continue expanding as more tools recognize Gherkin as a standard format. Version control systems, project management platforms, documentation generators, and analytics tools increasingly support Gherkin natively. This standardization reduces friction in toolchain integration and makes it easier for teams to adopt complementary tools.
The shift toward unified test management platforms reflects organizations' desire for comprehensive visibility without sacrificing technical flexibility. Teams want single sources of truth for test status while maintaining the freedom to use different automation approaches for different testing needs. Modern platforms achieve this by supporting multiple Gherkin frameworks, aggregating results, and providing unified reporting while letting teams optimize their technical implementations.
Gherkin Framework Comparison for Test Automation
Choosing the right framework for your gherkin automated testing depends on your technology stack, team expertise, and integration requirements. This comparison highlights key factors for common frameworks.
| Framework | Language Support | Primary Use Case | Integration Strength | Learning Curve | Best For |
| Cucumber | Java, JavaScript, Ruby, Kotlin, Go | General purpose BDD testing | Extensive plugin ecosystem, Selenium, Appium | Moderate | Teams with diverse language requirements |
| SpecFlow | C#, .NET | .NET application testing | Visual Studio, Azure DevOps, .NET testing tools | Moderate | Microsoft-stack development teams |
| Behave | Python | Python application testing | Python testing frameworks, pytest | Low | Python-focused development environments |
| JBehave | Java | Enterprise Java applications | Spring, Maven, Jenkins | Moderate-High | Large-scale Java enterprise systems |
| Codeception | PHP | PHP web application testing | Laravel, Symfony, WordPress | Low-Moderate | PHP development teams |
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between Gherkin and Cucumber? Gherkin is the language used to write test scenarios in a human-readable format using Given-When-Then syntax. Cucumber is a testing framework that reads Gherkin scenarios and executes them as automated tests by connecting them to step definitions. Gherkin provides the syntax while Cucumber provides the execution engine.
Can I use Gherkin for API testing or is it only for UI testing? Gherkin works excellently for API testing. The same Given-When-Then structure describes API test scenarios clearly. Step definitions connect to API testing libraries like REST Assured or HTTP client libraries. Many teams use Gherkin for comprehensive API testing because it makes expectations explicit and tests readable for both developers and product teams.
How do I convince my team to adopt Gherkin automated testing? Start with a pilot project covering a single feature or user journey. Demonstrate the collaboration benefits by including product owners in scenario creation. Show how Gherkin scenarios serve as living documentation that stays current. Highlight the maintenance advantages when UI changes don't break well-written declarative scenarios. Measure and share metrics around defects found earlier in the cycle and reduced rework from clearer requirements.
Does gherkin automation slow down test execution compared to traditional tests? Execution speed depends more on what tests do than how they're written. Gherkin scenarios that drive full UI automation run at the same speed as equivalent traditional UI tests. The abstraction layer adds minimal overhead. Teams optimize execution time through intelligent test selection using tags, parallel execution, and appropriate use of different test types. The maintainability benefits of Gherkin typically outweigh any minor execution overhead.
Ready to Transform Your Test Automation Strategy?
The evidence is clear that gherkin automated testing delivers measurable benefits for teams navigating modern software development challenges. The combination of readable specifications, executable tests, and collaborative development aligns perfectly with 2026's emphasis on speed, quality, and cross-functional teamwork.
Success requires more than just adopting Gherkin syntax. Teams need the right tooling to manage scenarios, execute tests, and track results across their development lifecycle. They need platforms that connect Gherkin feature files with requirements management, source control, and continuous integration pipelines.
TestQuality provides exactly this unified approach to gherkin automation and test management. Our platform natively imports Gherkin feature files, integrates with GitHub and Jira workflows, and centralizes automated test results from popular frameworks. Whether your team uses Cucumber, SpecFlow, or Behave, TestQuality brings all your testing efforts together in one place.
Transform your testing strategy with a platform purpose-built for modern development teams. Start your free TestQuality trial today and experience how unified test management accelerates delivery while improving software quality.