Key Takeaways
Test management DevOps integration creates a unified quality ecosystem that accelerates software delivery without compromising reliability.
Key insights:
- Organizations implementing integrated test management see up to 40% reduction in release delays
- Early bug detection reduces costs exponentially compared to fixing issues post-release
- Unified DevOps testing tools eliminate the quality-speed tradeoff through automation and real-time feedback
- Strategic test management integration transforms QA from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage
The bottom line: Teams that strategically integrate test management into their DevOps workflows achieve faster releases, reduce failures, and deliver higher-quality software.
The gap between development velocity and quality assurance continues to widen. Development teams push code multiple times per day while traditional testing approaches struggle to keep pace. The result? Bugs slip through, releases get delayed, and quality becomes negotiable rather than guaranteed.
According to Atlassian research, 99 percent of DevOps practitioners reported that DevOps had a positive impact on their organization, yet many still treat test management as an afterthought rather than a core DevOps component. This disconnect creates friction, slows delivery, and undermines the very agility DevOps promises.

Integrating test management with DevOps workflows isn't about adding more tools or running more tests. It's about creating a seamless quality ecosystem where testing happens continuously, feedback flows instantly, and quality insights drive every development decision.
Why Does Test Management Matter in DevOps?
DevOps fundamentally changed how we build software by breaking down silos between development and operations. But there's a critical third element that determines whether DevOps succeeds or fails: quality assurance.
Traditional test management operates in isolation. QA teams receive completed features, execute test suites, log bugs, and send everything back to development. This sequential approach creates bottlenecks that defeat the entire purpose of DevOps. When testing happens after development, it becomes a checkpoint rather than a continuous quality feedback mechanism.
Test management DevOps integration solves this problem by embedding quality validation throughout the development lifecycle. Instead of testing being a separate phase, it becomes an integral part of every code commit, pull request, and deployment. This shift transforms QA from a reactive function into a proactive quality driver.
The impact goes beyond speed. Integrated test management provides real-time visibility into software quality, helps teams make informed decisions about release readiness, and ensures that quality standards remain consistent across rapid development cycles. When test management aligns with DevOps principles, teams can move fast without breaking things.
What is Test Management DevOps Integration?
Test management DevOps integration represents the strategic alignment of testing processes, tools, and practices with continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines. Rather than treating test management as a standalone activity, integration embeds testing capabilities directly into development workflows.
This integration manifests in several key ways. First, test management systems connect directly with version control platforms like GitHub, allowing tests to execute automatically when developers commit code. Second, test management tools integrate with issue tracking systems like Jira, creating bidirectional traceability between requirements, test cases, and defects. Third, test execution happens within CI/CD pipelines, providing immediate feedback on code quality.
The technical implementation varies based on team needs, but the principle remains constant: testing becomes invisible infrastructure rather than a visible obstacle. Developers don't need to context-switch between tools or wait for separate testing phases. Quality validation happens automatically as part of their normal workflow.
Modern test management platforms designed for DevOps support this integration through APIs, webhooks, and native connections to popular DevOps tools. These integrations enable automated test creation, execution, reporting, and result aggregation without manual intervention. The goal is making quality feedback as immediate and actionable as compilation errors.
How Does DevOps Testing Transform Software Delivery?
DevOps testing fundamentally reimagines the relationship between development speed and software quality. Traditional testing approaches force teams to choose between moving fast and maintaining quality standards. DevOps QA eliminates this false choice through automation, continuous feedback, and intelligent test management.
The transformation starts with shift-left principles. Rather than discovering defects late in the development cycle, DevOps testing pushes quality validation earlier, catching issues when they're easiest and cheapest to fix. Unit tests run with every code change. Integration tests validate component interactions immediately. Performance tests identify bottlenecks before they reach production.
According to research by Black Duck, the Systems Sciences Institute at IBM reported that fixing bugs during implementation costs 6x more than fixing those identified during design, and bugs found during testing can cost 15x more than those caught early. This economic reality makes early testing not just a quality practice but a business imperative. DevOps testing tools automate this early detection, running thousands of tests in minutes and surfacing issues while developers still have context.
Beyond cost savings, DevOps testing enables true continuous delivery. Automated test suites act as quality gates in deployment pipelines, ensuring only validated code reaches production. When tests pass, deployments proceed automatically. When tests fail, pipelines halt and notify relevant team members immediately. This automated quality validation removes human bottlenecks while maintaining rigorous standards.
The cultural shift matters as much as the technical one. DevOps testing breaks down the traditional wall between developers and testers, creating shared responsibility for quality. Developers write unit tests. QA engineers design automation frameworks. Operations teams monitor production behavior. Everyone contributes to the testing strategy, and everyone benefits from faster, more reliable releases.
Continuous testing DevOps approaches also generate valuable quality metrics. Test coverage percentages, pass rates, execution times, and defect trends provide objective data about software health. Teams use these metrics to make informed decisions about release readiness, identify risky areas requiring additional testing, and track quality improvements over time.
Essential DevOps Testing Tools for Modern Teams
Building an effective DevOps testing ecosystem requires the right combination of tools working in harmony. Each tool serves a specific purpose while integrating with others to create a comprehensive testing solution.

Version Control Integration Tools
Version control systems like GitHub and GitLab form the foundation of DevOps workflows. Test management platforms that integrate directly with these systems enable automated test execution on pull requests, branch deployments, and merge events. This integration ensures code quality validation happens before changes enter the main codebase.
Continuous Integration Platforms
Jenkins, CircleCI, and Azure DevOps provide the automation infrastructure that powers DevOps pipelines. These platforms orchestrate build processes, execute test suites, and manage deployment workflows. The test automation market demonstrates rapid growth, valued at USD 25.4 billion in 2024 and projected to reach USD 216.6 billion by 2037, with a CAGR of 17.2 percent. The best CI platforms support parallel test execution, reducing feedback time from hours to minutes.
Test Automation Frameworks
Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress dominate browser-based testing, while tools like JUnit and TestNG handle unit testing. These frameworks provide the technical foundation for automated test execution. However, frameworks alone don't constitute test management. They need orchestration, reporting, and integration with other DevOps tools to deliver value.
Test Management Platforms
Unified test management platforms are essential for bridging the gap between test automation frameworks and DevOps workflows. They provide centralized test case repositories, execution tracking, result aggregation, and crucial requirement traceability. The most effective platforms integrate seamlessly with version control, issue tracking, and CI/CD tools, fostering a truly connected and efficient testing ecosystem.
API Testing Tools
As microservices architectures proliferate, API testing becomes increasingly critical. Tools like Postman, SoapUI, and REST Assured validate service contracts, test integration points, and verify API behavior under various conditions. DevOps QA strategies incorporate API testing throughout development cycles, not just during pre-release validation.
Performance Testing Solutions
JMeter, Gatling, and K6 enable performance testing within DevOps pipelines. These tools simulate load conditions, identify performance bottlenecks, and validate scalability. Integrating performance tests into continuous testing DevOps approaches prevents performance regressions and ensures applications meet non-functional requirements.
Security Testing Tools
DevSecOps extends DevOps principles to include security validation. Tools like OWASP ZAP, Snyk, and Checkmarx scan code for vulnerabilities, check dependencies for known security issues, and validate authentication mechanisms. Security testing integration ensures applications remain secure throughout rapid development cycles.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Slack, Microsoft Teams, and similar platforms enable real-time communication about test results, failures, and quality trends. Integrating test management systems with communication tools ensures the right people receive instant notifications about quality issues requiring attention.
The key to DevOps testing tools success lies not in accumulating tools but in creating a cohesive ecosystem where tools work together seamlessly. Integration eliminates manual data transfer, reduces context switching, and ensures quality information flows freely across the development organization.
What Are the Key Components of DevOps QA?
DevOps QA succeeds through several interconnected components working together to ensure continuous quality validation. Understanding these components helps teams build comprehensive testing strategies that support rapid development without sacrificing reliability.
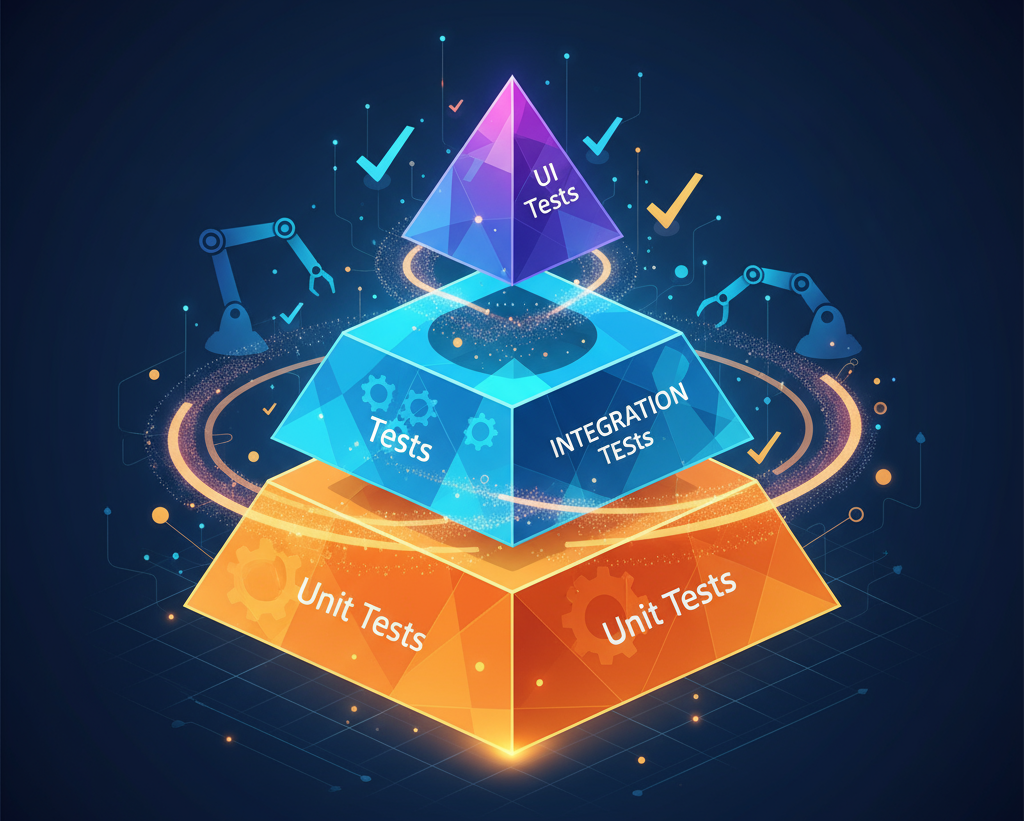
Automated test execution forms the foundation of DevOps QA. Manual testing simply cannot keep pace with multiple daily deployments. Automation enables teams to run extensive test suites quickly, repeatedly, and consistently. The key is automating the right tests at the right levels, following the testing pyramid principle where unit tests form the base, integration tests occupy the middle, and UI tests sit at the top.
Test data management represents another critical component often overlooked in DevOps implementations. Tests require realistic data to validate application behavior effectively. DevOps QA strategies include mechanisms for generating, maintaining, and refreshing test data across environments. Poor test data leads to false positives, missed defects, and unreliable test results that undermine confidence in automated testing.
Continuous feedback mechanisms ensure quality information reaches relevant stakeholders immediately. When tests fail, developers receive instant notifications with detailed failure information. When quality metrics trend negatively, team leads get alerts. When release quality meets standards, stakeholders get confidence to proceed with deployments. Effective feedback loops accelerate issue resolution and prevent quality problems from compounding.
Environment management ensures tests run in conditions that accurately reflect production. Infrastructure as Code tools like Terraform and Ansible enable teams to create consistent, reproducible test environments. Environment parity reduces the "works on my machine" problem and increases confidence that test results predict production behavior.
Traceability connects requirements, test cases, and defects throughout the development lifecycle. Teams need visibility into which requirements have test coverage, which tests validate specific functionality, and how defects relate to failed tests. Strong traceability practices improve requirement validation, simplify impact analysis, and support compliance needs.
Quality metrics and reporting provide objective insights into software health. Code coverage percentages indicate how thoroughly tests exercise the codebase. Defect density metrics highlight problematic areas requiring additional attention. Test execution trends reveal whether test suites grow too large or slow. These metrics inform decisions about testing strategy, resource allocation, and release readiness.
Risk-based testing prioritizes test execution based on business impact and change risk. Not all features carry equal weight, and not all code changes pose equal risk. DevOps QA approaches use risk assessment to focus testing effort where it matters most, balancing comprehensive validation with speed requirements.
How to Implement Continuous Testing DevOps Successfully
Implementing continuous testing DevOps requires strategic planning, gradual adoption, and continuous refinement. Teams cannot transform testing practices overnight, but they can follow a structured approach to build momentum and demonstrate value.
Start by assessing your current testing maturity. Document existing test processes, identify manual bottlenecks, and evaluate current tool capabilities. Understanding the starting point helps teams set realistic goals and measure progress. Many organizations discover they have more manual testing than they realized and limited automation infrastructure.
Define clear objectives aligned with business goals. Are you trying to reduce release cycle time? Improve defect detection rates? Increase deployment confidence? Decrease testing costs? Specific objectives guide tool selection, process changes, and success metrics. Vague goals like "improve testing" fail to provide direction or demonstrate value.
Select tools that integrate seamlessly with existing DevOps infrastructure. The best test management platform integrates with your version control system, CI/CD pipeline, and issue tracker without requiring extensive custom development. Tool integration determines whether test management enhances or hinders developer productivity.
Implement test automation incrementally using the testing pyramid as a guide. Start with unit tests that validate individual components. Expand to integration tests that verify component interactions. Finally, add UI tests for critical user journeys. This progression builds confidence in automation while maintaining manageable test execution times.
Establish coding standards for test automation. Tests are code and require the same quality standards as production code. Code reviews, version control, and modular design principles apply equally to test automation. Poor test code quality leads to fragile tests, difficult maintenance, and reduced confidence in test results.
Create a culture of quality ownership where everyone shares responsibility for testing. Developers write unit tests and fix issues their code introduces. QA engineers design automation frameworks and validate complex scenarios. Operations teams monitor production behavior and feed insights back to development. Shared ownership prevents testing from becoming a single team's bottleneck.
Integrate tests into CI/CD pipelines progressively. Begin with smoke tests that validate basic functionality. Add regression tests that protect against known issues. Incorporate performance tests that validate scalability. Build security tests that detect vulnerabilities. Each integration provides additional quality validation without significant pipeline delays.
Monitor and optimize test execution continuously. Track test execution times, failure rates, and maintenance effort. Identify flaky tests that fail intermittently and either fix or remove them. Optimize slow tests that delay feedback. Prune obsolete tests that validate deprecated functionality. Continuous optimization keeps test suites fast, reliable, and valuable.
Provide comprehensive training and documentation. Team members need to understand test management DevOps integration principles, tool capabilities, and best practices. Documentation should cover test creation, execution, result interpretation, and troubleshooting. Invest in training to ensure teams can leverage continuous testing DevOps capabilities effectively.
Best Practices for Test Management DevOps Integration
Successful test management DevOps integration requires following established best practices that balance automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. These practices help teams avoid common pitfalls while maximizing the value of integrated testing.

The table below outlines essential practices and their impact:
| Practice | Description | Key Benefit |
| Shift Testing Left | Begin testing activities during requirements and design phases | Catch defects when they're least expensive to fix |
| Automate Repetitive Tests | Prioritize automation for regression, smoke, and API testing | Reduce test execution time significantly |
| Integrate with Version Control | Trigger tests automatically on code commits and pull requests | Validate quality before code enters main branch |
| Implement Parallel Execution | Run tests concurrently across multiple environments | Cut feedback time from hours to minutes |
| Maintain Test Data | Create realistic, representative test data sets | Improve defect detection accuracy |
| Use Risk-Based Prioritization | Focus testing effort on high-risk, high-impact areas | Maximize quality ROI with limited resources |
Beyond these core practices, several additional guidelines enhance test management DevOps effectiveness. First, maintain clear separation between test layers. Unit tests validate individual components in isolation. Integration tests verify component interactions. End-to-end tests validate complete user workflows. Mixing test purposes creates confusion and reduces test suite maintainability.
Second, design tests for resilience and stability. Flaky tests that pass and fail unpredictably erode confidence in automation. Invest time making tests deterministic, properly isolating test data, and handling timing issues correctly. A smaller suite of reliable tests provides more value than a large collection of unreliable ones.
Third, treat test code with the same rigor as production code. Apply code review processes, follow coding standards, and refactor tests regularly. Technical debt accumulates in test suites just as it does in production code, eventually making tests difficult to maintain and understand.
Fourth, establish clear ownership and accountability for test failures. When tests fail, someone needs to investigate quickly and determine whether the failure indicates a real defect or a test issue. Unclear ownership leads to ignored failures and diminished trust in automated testing.
Fifth, balance test coverage with execution speed. Comprehensive coverage provides confidence but slow tests delay feedback and reduce developer productivity. Find the sweet spot where tests provide adequate validation without creating deployment bottlenecks.
Sixth, integrate testing with observability and monitoring. Production monitoring provides insights that inform testing strategy. Common production errors suggest gaps in test coverage. Performance metrics validate whether performance tests reflect real-world behavior. The feedback loop between production and testing continuously improves quality validation.
Finally, measure and communicate testing value. Track metrics like defect escape rate, mean time to detect issues, and test coverage trends. Share these metrics with stakeholders to demonstrate how test management DevOps integration improves software quality and delivery speed. Visible value ensures continued investment and support for testing initiatives.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing test management DevOps integration presents several challenges that teams must navigate successfully. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions helps organizations avoid common implementation pitfalls.
Test environment management often becomes a major bottleneck. Creating and maintaining environments that accurately mirror production requires significant effort. Inconsistent environments lead to false test results and the infamous problem of tests passing in test environments but failing in production. Solutions include infrastructure as code approaches that automate environment provisioning, containerization technologies that ensure environment consistency, and service virtualization that simulates complex dependencies.
Test data management complexity grows as applications become more sophisticated. Tests need realistic data reflecting production scenarios, but production data often contains sensitive information unsuitable for test environments. Creating and maintaining synthetic test data requires ongoing effort. Solutions include data masking tools that anonymize production data, test data generation tools that create realistic synthetic data, and data subset strategies that extract relevant portions of production databases.
Tool integration challenges emerge when connecting multiple DevOps testing tools into a cohesive ecosystem. APIs may not expose all necessary functionality. Authentication between systems creates security concerns. Data synchronization between tools requires careful mapping. Solutions include selecting tools with robust integration capabilities, leveraging integration platforms that connect disparate systems, and accepting that some manual processes may remain necessary.
Flaky tests undermine confidence in automated testing and waste developer time investigating false failures. Network timing issues, race conditions, and environmental dependencies cause tests to behave unpredictably. Solutions include implementing explicit waits instead of fixed sleeps, properly isolating test data between test runs, and maintaining separate test stability metrics that identify problematic tests requiring attention.
Test maintenance burden increases as test suites grow larger and applications evolve. Every application change potentially breaks existing tests. Large test suites become difficult to understand, modify, and debug. Solutions include regular test refactoring to improve maintainability, automated test impact analysis that identifies which tests need updates after code changes, and ruthless test pruning that removes obsolete or low-value tests.
Cultural resistance to quality ownership can derail DevOps QA initiatives. Developers may resist writing tests, viewing testing as someone else's responsibility. QA engineers may resist automation, fearing job security implications. Solutions include leadership emphasis on shared quality ownership, recognition and rewards for quality contributions, and training that builds testing skills across all roles.
Skills gaps limit test automation effectiveness. Writing maintainable, reliable automated tests requires different skills than manual testing. Not all QA engineers have programming backgrounds. Not all developers understand testing best practices. Solutions include comprehensive training programs, pairing QA engineers with developers during test automation development, and selecting test tools that match team skill levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between DevOps testing and traditional testing?
DevOps testing integrates quality validation continuously throughout development, while traditional testing occurs as a separate phase after development completes. DevOps testing emphasizes automation, rapid feedback, and shared quality ownership across development and operations teams. Traditional testing relies more heavily on manual processes, sequential workflows, and dedicated QA teams operating independently from development.
How do you integrate test automation with CI/CD pipelines?
Integration happens through several mechanisms. First, connect your test management platform to your CI/CD tool via API or native integration. Second, configure pipeline triggers that execute test suites on code commits, pull requests, or scheduled intervals. Third, establish quality gates that prevent deployments when critical tests fail. Fourth, route test results back to developers through integration with communication and issue tracking tools. The goal is making test execution automatic and feedback immediate.
What percentage of tests should be automated in DevOps?
The optimal automation percentage depends on your application, team skills, and release frequency. Follow the testing pyramid principle: automate most unit tests (70-80 percent), automate fewer integration tests (15-20 percent), and automate only critical UI tests (5-10 percent). Prioritize automation for regression tests, smoke tests, and API tests that run frequently. Some exploratory and usability testing may remain manual. Focus on automating tests that provide the highest value relative to maintenance cost.
How does test management improve DevOps collaboration?
Test management platforms create shared visibility into quality status, making testing transparent across development, QA, and operations teams. Integrated platforms connect requirements to test cases to defects, enabling everyone to understand what's being tested and why. Real-time test execution results flow to all stakeholders, eliminating information silos. Centralized test repositories ensure everyone works from the same test definitions. This transparency and shared information foundation enables true collaboration around quality goals.
What metrics should teams track for DevOps testing?
Key metrics include test automation coverage percentage, test execution time, test pass rates, defect escape rate to production, mean time to detect defects, and test maintenance effort. Track these metrics over time to identify trends. Monitor flaky test rates to ensure test reliability. Measure deployment frequency and lead time to correlate testing practices with delivery speed. Quality metrics should inform decisions about testing strategy, tool investments, and process improvements.
Get Started with Integrated Test Management Today
Test management DevOps integration transforms quality from a bottleneck into an accelerator. Organizations that successfully integrate testing with DevOps workflows deliver software faster, with fewer defects, and with greater confidence. The technical challenges are real but surmountable. The cultural shifts require commitment but pay dividends.
The key lies in starting strategically rather than attempting overnight transformation. Begin with clear objectives, select tools that integrate naturally with existing DevOps infrastructure, and build momentum through incremental wins. Focus on automation that provides immediate value, establish quality ownership across teams, and continuously refine testing practices based on results.
Success requires more than tools and processes. It requires a platform designed specifically for DevOps workflows, one that understands the importance of seamless integration, real-time feedback, and collaborative quality ownership.
For those seeking a platform purpose-built to bridge the gap between robust test management and efficient DevOps workflows, consider solutions like TestQuality. With native integrations to essential tools such as GitHub, Jira, and leading CI/CD platforms, such a platform seamlessly embeds quality validation directly into your development pipeline. From comprehensive test planning and execution to insightful reporting, these capabilities are designed to support the speed and collaboration that modern DevOps demands. Explore how a unified test management solution can accelerate your delivery without compromising quality.