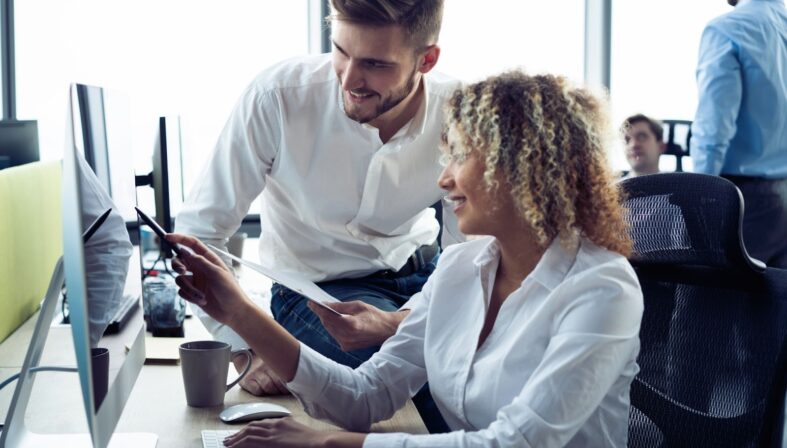
Poor software quality continues to cost the U.S. economy billions annually, with recent research from CISQ demonstrating that early defect detection significantly reduces these economic impacts. Yet most development teams still discover critical issues only days before release deadlines.
This reactive approach to quality assurance creates unnecessary stress, budget overruns, and delayed product launches that could be prevented through effective test plan management integrated with shift-left testing methodologies.
The shift-left approach moves testing activities earlier in the development lifecycle, enabling teams to identify and resolve issues when they're cheapest and easiest to fix. However, successful implementation requires sophisticated test management tools that can coordinate early testing activities, maintain traceability, and provide actionable insights throughout the development process, enabling teams to effectively manage their test plans.
This comprehensive guide explores how modern test management tools enable effective shift-left testing, providing practical strategies for implementation and optimization.
What is Test Plan Management in Shift-Left Testing?
Test plan management in shift-left testing represents a fundamental shift from traditional testing approaches. Instead of treating quality assurance as a final validation step, teams integrate comprehensive testing strategies from the earliest stages of development.
Defining Modern Test Plan Management
Contemporary test plan management encompasses far more than traditional test case documentation. It involves strategic coordination of testing activities across the entire development lifecycle, ensuring that quality considerations influence design decisions, requirement specifications, and implementation approaches.
Effective test plan management creates a framework for early risk identification, automated test integration, and continuous feedback loops that keep development teams informed about quality status throughout the project lifecycle.
The Cost of Late Testing
The financial impact of delayed testing extends far beyond simple bug fixing costs. Organizations implementing shift-left testing strategies typically report fewer post-release defects and faster time-to-market compared to traditional testing approaches.
Late-stage testing creates cascading problems: rushed fixes introduce new bugs, delayed releases impact revenue, and stressed teams make poor decisions under pressure. These issues compound when testing activities compete with release deadlines rather than supporting them. IBM's comprehensive analysis of shift-left testing confirms that proactive testing approaches significantly outperform reactive strategies in both cost and quality metrics.
Shift-Left Benefits for Quality Teams
Early testing integration transforms quality assurance from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage. Teams practicing effective shift-left testing report improved collaboration between developers and testers, better requirement clarity, and more predictable release schedules.
Modern test management platforms enable this transformation by providing unified environments where early testing activities integrate seamlessly with development workflows, creating comprehensive visibility into quality status throughout the project lifecycle.
7 Essential Test Plan Management Strategies for Shift-Left Success
Implementing shift-left testing requires deliberate strategies that address the unique challenges of early testing integration.
1. Early Requirement Analysis and Test Planning
Successful shift-left implementation begins during requirement gathering. Test considerations must influence requirement specifications, ensuring that testability becomes a design criterion rather than an afterthought.
This approach involves creating testable acceptance criteria, identifying potential testing challenges early, and establishing clear quality gates that align with development milestones. Advanced test case management systems support this process by linking requirements directly to test specifications.
2. Risk-Based Test Prioritization
Early testing requires intelligent prioritization since testing everything immediately is neither practical nor cost-effective. Risk-based approaches focus testing efforts on areas with the highest potential impact, ensuring that limited early-stage testing resources address the most critical quality concerns.
Effective prioritization considers business impact, technical complexity, and change frequency to create testing strategies that maximize quality assurance value while minimizing resource investment.
3. Automated Test Integration Planning
Automation becomes crucial in shift-left environments where testing frequency increases dramatically. However, automation strategies must be planned carefully to avoid creating maintenance overhead that undermines shift-left benefits.
Successful automation integration involves selecting appropriate tools, designing maintainable test architectures, and establishing clear boundaries between automated and manual testing activities.
4. Continuous Feedback Loop Implementation
Shift-left testing succeeds through rapid feedback cycles that inform development decisions in real-time. This requires establishing clear communication channels between testing activities and development teams, ensuring that quality information reaches decision-makers quickly.
Modern test management platforms facilitate these feedback loops by providing real-time dashboards, automated notifications, and integration with development tools that developers use daily.
5. Cross-Functional Team Collaboration
Early testing success depends on breaking down traditional silos between development, testing, and business stakeholders. This collaborative approach requires tools and processes that enable effective communication across different skill levels and technical backgrounds.
Platforms that support both technical test automation and business-readable reporting enable broader team participation in quality assurance activities.
6. Test Data Management Strategy
Early testing often occurs in environments with limited or incomplete test data. Effective test data strategies ensure that meaningful testing can occur throughout the development lifecycle, even when full production-like datasets are unavailable.
This involves creating synthetic test data, establishing data refresh procedures, and maintaining data privacy and security throughout the testing process.
7. Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Shift-left testing generates significantly more testing activity than traditional approaches. Teams must monitor testing performance to ensure that increased testing frequency doesn't slow development velocity or create resource bottlenecks.
Effective monitoring involves tracking test execution times, identifying automation maintenance requirements, and optimizing testing workflows for maximum efficiency.
Modern test management platforms, such as TestQuality, are designed to facilitate these strategies by providing unified environments for early testing, comprehensive visibility, and seamless integration with development workflows.
Tool Selection for Effective Test Plan Management
Choosing appropriate tools becomes critical when implementing shift-left testing strategies. The wrong tools can create more overhead than value, while the right platforms enable seamless integration of early testing activities.
Essential Tool Categories
Effective shift-left testing requires integration across multiple tool categories. Test management platforms must coordinate with development environments, automation frameworks, and business communication tools to create unified workflows.
Key categories include test case management, automation orchestration, requirement traceability, defect tracking, and reporting systems. The most effective implementations use platforms that integrate these capabilities rather than attempting to coordinate separate tools.
Integration Requirements with Development Tools
Modern development teams rely heavily on tools like GitHub for version control and Jira for project management. Shift-left testing success requires seamless integration with these existing workflows rather than creating parallel processes.
Specialized test management solutions that integrate natively with development tools eliminate context switching and ensure that testing activities remain synchronized with development progress. TestQuality, for example, offers native integrations with popular development tools like GitHub and Jira, simplifying workflow coordination and enhancing team efficiency.
Evaluation Criteria for 2025
Contemporary tool evaluation must consider cloud-native architectures, AI-assisted testing capabilities, and support for modern development methodologies like DevOps and continuous deployment.
Teams should prioritize platforms that support rapid scaling, provide comprehensive APIs for custom integrations, and offer flexibility to adapt to evolving testing requirements.
Implementing Test Plan Management in Your Shift-Left Strategy
Successful shift-left implementation requires careful planning and gradual rollout to avoid disrupting existing development workflows while building new testing capabilities.
Getting Started: Assessment and Planning
Implementation begins with honest assessment of current testing capabilities, team skills, and existing tool investments. This assessment identifies gaps that must be addressed and strengths that can be leveraged during transition.
Effective planning establishes realistic timelines, identifies training requirements, and creates success metrics that demonstrate progress toward shift-left goals.
Gradual Implementation Approach
Rather than attempting complete transformation immediately, successful teams implement shift-left testing gradually. This approach allows teams to learn and adapt while maintaining productivity and avoiding disruption to critical development activities.
Gradual implementation often begins with pilot projects that demonstrate value before expanding to broader development activities.
Team Training and Change Management
Shift-left testing requires new skills and different workflows for both developers and testers. Effective training programs address technical tool usage as well as collaborative processes that enable early testing success.
Change management becomes crucial for overcoming resistance and ensuring that new processes become embedded in team culture rather than abandoned when challenges arise.
AI and Machine Learning in Test Plan Management
Modern test management platforms increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities that enhance shift-left testing effectiveness.
Predictive Test Selection
AI-powered platforms can analyze code changes and automatically identify which tests should be executed to provide optimal coverage with minimal resource investment. This capability becomes crucial in shift-left environments where testing frequency increases dramatically.
Predictive selection reduces testing time while maintaining confidence in quality assurance coverage.
Automated Risk Assessment
Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical defect patterns, code complexity metrics, and change frequency to automatically identify high-risk areas that require additional testing attention.
This automated analysis supplements human judgment with data-driven insights that improve testing effectiveness and resource allocation.
Intelligent Test Maintenance
AI capabilities can identify flaky tests, suggest test case improvements, and automatically update test scripts when application interfaces change. Advanced unit testing frameworks reduce the maintenance overhead that often undermines automation initiatives.
Intelligent maintenance ensures that automated testing remains valuable rather than becoming a burden that slows development velocity.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Shift-Left Test Management
Effective measurement enables teams to validate shift-left benefits and identify areas for continued improvement.
 Quality Metrics That Matter
Quality Metrics That Matter
Traditional quality metrics often focus on post-development activities like defect discovery rates and test execution results. Shift-left testing requires additional metrics that capture early-stage quality activities and their impact on overall development effectiveness.
Key metrics include defect prevention rates, requirement testability scores, and early feedback cycle times. Comprehensive quality metrics frameworks help teams track progress toward shift-left goals.
Cost and Time Savings Tracking
Shift-left testing investments should generate measurable returns through reduced rework, faster development cycles, and improved predictability. Tracking these benefits requires careful measurement of both traditional costs and opportunity costs associated with delayed quality feedback.
Effective tracking demonstrates ROI and justifies continued investment in shift-left capabilities.
Team Productivity Indicators
Successful shift-left implementation should improve rather than hinder team productivity. Metrics like development velocity, deployment frequency, and team satisfaction indicate whether shift-left practices are creating value or overhead.
Regular monitoring ensures that testing improvements contribute to overall development effectiveness.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Test Plan Management
Shift-left testing implementation faces predictable challenges that can be addressed through careful planning and appropriate tool selection.
Resource Allocation Issues
Early testing requires upfront investment in tools, training, and process development. Teams often struggle to justify this investment when immediate benefits aren't apparent.
Successful implementations address resource concerns by demonstrating quick wins, phasing implementation to spread costs over time, and clearly communicating long-term benefits to stakeholders.
Tool Integration Complexity
Integrating testing activities with existing development workflows can create significant technical challenges. Teams may struggle with tool compatibility, data synchronization, and workflow coordination.
Strategic test planning approaches address these challenges by providing native integrations and unified interfaces that eliminate coordination overhead.
Cultural Resistance to Change
Shift-left testing requires changes to established workflows and responsibilities. Team members may resist new processes, especially when they increase immediate workload without obvious benefits.
Effective change management addresses resistance through clear communication, comprehensive training, and visible leadership support for new approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the ROI timeframe for shift-left test plan management?
Most organizations see initial ROI within 3-6 months through reduced rework and faster issue resolution. Full benefits typically materialize within 12-18 months as teams develop proficiency with new processes and tools.
How do you prioritize tests in early development stages?
Risk-based prioritization focuses on areas with highest business impact, technical complexity, and change frequency. Start with core functionality and gradually expand coverage as development progresses.
Which tools integrate best with existing development workflows?
Platforms with native GitHub and Jira integration provide the smoothest transition. Look for tools that support existing development team workflows rather than requiring separate processes.
How do you measure the effectiveness of shift-left testing?
Track metrics like defect prevention rates, early feedback cycle times, development velocity, and post-release defect rates. Compare these metrics before and after shift-left implementation to demonstrate impact.
Final Thoughts: Building a Sustainable Test Plan Management Practice
Shift-left testing represents more than a process change—it's a fundamental shift toward proactive quality assurance that prevents problems rather than just detecting them. Success requires appropriate tools, comprehensive planning, and sustained commitment to new workflows and collaboration patterns.
The most successful implementations recognize that test plan management becomes the coordination mechanism that enables effective shift-left testing. By investing in platforms that support early testing activities while integrating seamlessly with development workflows, teams can achieve the full benefits of shift-left approaches.
Start with clear goals, implement gradually, and measure progress consistently. The investment in effective test plan management will pay dividends through improved quality, faster development cycles, and more predictable product releases.
Ready to transform your testing strategy with comprehensive shift-left test plan management? TestQuality provides the integrated platform and features necessary to support early testing activities, streamline workflows, and help teams achieve improved quality, faster development cycles, and more predictable product releases. Visit TestQuality.com to learn more about how our solution can support your shift-left initiatives.