Key Takeaways
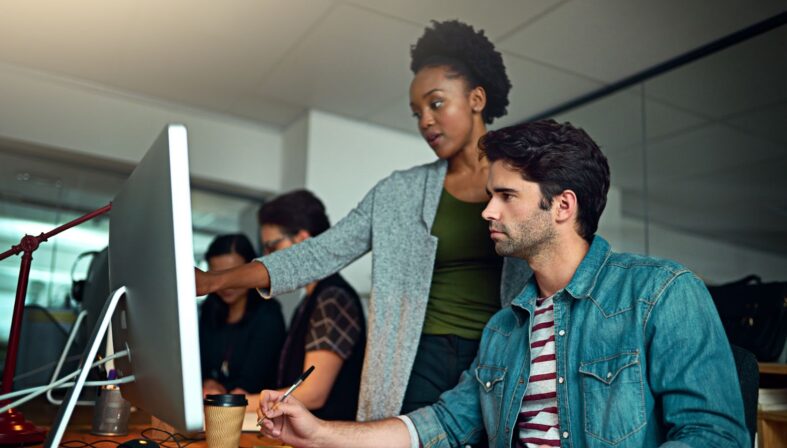
Exploratory test management bridges the gap between unscripted testing creativity and systematic quality assurance processes.
- Session-based test management provides structure while preserving the flexibility that makes exploratory testing valuable
- Modern QA teams use exploratory methods to uncover 40% more critical defects than scripted testing alone
- Integration with test management platforms transforms ad-hoc findings into actionable insights and repeatable processes
Strategic exploratory QA approaches enhance software quality while supporting faster development cycles
When software quality issues cost the U.S. economy at least $2.41 trillion annually, QA teams need testing approaches that are both thorough and adaptable. Structured exploratory testing represents the evolution of traditional ad-hoc testing into a valuable component of comprehensive quality assurance strategies.
Unlike purely scripted testing methods, this approach combines the investigative power of human intuition with systematic documentation and analysis. This approach has become increasingly critical as manual testing services grow to an expected $8.2 billion market by 2033, driven by the need for nuanced, user-focused test management solutions.
The rise of structured exploratory testing reflects a broader shift in software development philosophy. Teams are recognizing that while automation handles repetitive tasks effectively, human creativity and domain expertise remain irreplaceable for uncovering edge cases, usability issues, and unexpected system behaviors that could impact user experience.
What Is Exploratory Test Management?
A systematic approach to conducting, organizing, and leveraging exploratory testing within broader quality assurance frameworks transforms the traditionally unstructured nature of exploratory testing into a manageable, measurable, and repeatable process that delivers consistent value to development teams.
At its core, this methodology maintains the investigative spirit of traditional exploratory testing while adding crucial elements of planning, documentation, and analysis. Testers simultaneously design and execute tests based on their understanding of the software, but within a framework that captures insights, tracks coverage, and enables knowledge sharing across teams.
This approach addresses a fundamental challenge in modern software development: the need for both speed and quality. Multiple industry studies indicate that time constraints consistently rank as the primary challenge facing development teams, making structured exploratory approaches essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
How Has Testing Evolved From Ad-Hoc Methods?
Traditional ad-hoc testing often suffered from poor documentation, inconsistent coverage, and difficulty in reproducing discovered issues. This structured approach evolves traditional methods by introducing session-based methodologies, clear objectives, and integration with formal test planning processes.
Modern exploratory testing incorporates time-boxing, charter-driven sessions, and systematic debriefing processes that transform individual testing insights into team knowledge. This structured approach enables organizations to harness the creativity and domain expertise of their QA professionals while maintaining the accountability and traceability required for enterprise software development.
What Are the Core Components of Effective Exploratory Test Management?
Building a successful exploratory testing framework requires several foundational elements working together harmoniously. These components provide the structure needed to transform ad-hoc testing into a systematic, repeatable process while preserving the investigative creativity that makes exploratory testing valuable.
How Does Session-Based Test Management Work?
Session-Based Test Management forms the backbone of effective exploratory test management. SBTM structures exploratory testing into focused, time-boxed sessions guided by specific charters or missions. Each session typically lasts 60-120 minutes and focuses on particular features, user scenarios, or risk areas.
The SBTM approach includes five key phases: charter definition, session execution, note-taking and documentation, review and analysis, and team debriefing. This structure ensures that exploratory efforts remain focused while preserving the flexibility that makes this testing approach valuable.
Session charters serve as lightweight mission statements that provide direction without constraining tester creativity. A well-crafted charter might specify "Explore the checkout process with focus on payment validation, using various card types and edge cases, to discover usability issues and functional defects." This guidance helps testers maintain focus while encouraging thorough investigation.
Documentation and Knowledge Capture
Effective documentation strategies that capture both explicit findings and tacit knowledge gained during testing sessions are essential for structured exploratory approaches. This includes not only defects discovered but also insights about user experience, system performance, and areas requiring additional attention.
Modern documentation approaches leverage multiple formats including screenshots, screen recordings, mind maps, and structured notes. The goal is creating searchable, shareable knowledge repositories that enable team members to build upon previous explorations and avoid duplicate effort.
Many teams supplement traditional documentation with collaborative approaches such as pair testing, where two testers work together to explore software while simultaneously documenting findings. This approach not only improves documentation quality but also facilitates knowledge transfer and reduces the risk of overlooking critical issues.
Test Charter Development
Test charters provide strategic direction for exploratory sessions without imposing rigid constraints on tester creativity. Effective charters balance specificity with flexibility, offering enough guidance to maintain focus while preserving the investigative freedom that makes exploratory testing valuable.
Charter development should involve multiple stakeholders including product owners, developers, and experienced testers. This collaborative approach ensures that exploratory efforts align with business priorities while leveraging technical expertise to identify high-risk areas requiring investigation.
Well-designed charters typically include three key elements: the area or feature to explore, specific risks or scenarios to investigate, and resources or constraints that might impact testing. For example, "Explore mobile app navigation using various device orientations and network conditions to identify usability issues and performance bottlenecks."
What Are the Benefits of Implementing Exploratory Test Management?
Systematic exploratory testing delivers measurable improvements across multiple aspects of software quality and development efficiency. Teams that adopt systematic exploratory approaches typically see enhanced defect detection capabilities, faster feedback cycles, and improved test coverage compared to traditional testing methods alone.
Enhanced Defect Discovery
Industry experience consistently shows that exploratory testing uncovers different types of defects than scripted testing, particularly in areas of user experience, edge cases, and system integration. The investigative nature of exploratory approaches enables testers to follow unexpected paths and discover issues that predetermined test cases might miss.
This approach amplifies these benefits by ensuring that discoveries are properly documented, analyzed, and integrated into broader quality assurance strategies. Teams implementing structured exploratory approaches consistently report finding critical defects that automated and scripted testing miss.
The human creativity and domain expertise inherent in exploratory testing proves particularly valuable for identifying usability issues, accessibility concerns, and real-world usage scenarios that automated tests cannot effectively simulate. This capability becomes increasingly important as software applications become more complex and user expectations continue to rise.
Faster Feedback Cycles
Exploratory testing enables rapid feedback during development cycles, particularly valuable in agile and DevOps environments where quick iteration is essential. Unlike scripted testing approaches that require extensive preparation and planning, exploratory sessions can begin immediately when new functionality becomes available.
This speed advantage proves particularly valuable during early development phases when requirements may still be evolving. Exploratory testing provides immediate insights into software behavior, enabling developers to address issues before they become costly to fix. Research from the IBM Systems Sciences Institute indicates that addressing defects during development costs significantly less than fixing them in production.
The rapid feedback enabled by exploratory approaches also facilitates better collaboration between development and QA teams. Testers can provide immediate insights about user experience, functional behavior, and potential risks, enabling developers to make informed decisions about implementation approaches and priorities.
Improved Test Coverage
While exploratory testing might seem less systematic than scripted approaches, properly managed exploratory efforts often achieve superior test coverage by investigating areas that predetermined test cases might overlook. The investigative nature of exploratory testing leads testers to explore edge cases, error conditions, and integration points that formal test planning might miss.
This structured approach enhances coverage by ensuring that sessions are strategically planned to address different risk areas, user scenarios, and system components. Session charters help distribute exploratory efforts across the application while documentation practices ensure that coverage gaps are identified and addressed.
Many organizations combine exploratory and scripted testing approaches to achieve comprehensive coverage. Scripted tests handle known scenarios and regression testing while exploratory sessions investigate new functionality, edge cases, and user experience concerns.
What Are the Key Strategies for Successful Implementation?
Implementing exploratory testing effectively requires strategic planning and systematic execution across multiple dimensions. Successful organizations focus on three critical areas: risk-based prioritization, structured time management, and cross-functional collaboration to maximize the value of their exploratory testing investments.
Risk-Based Test Planning
Effective exploratory test management requires strategic planning that focuses effort on areas of highest risk and business impact. This risk-based approach ensures that limited testing resources are allocated to areas where defects would have the most significant consequences.
Risk assessment should consider multiple factors including business criticality, technical complexity, recent code changes, and historical defect patterns. Areas identified as high-risk receive more exploratory attention through longer sessions, more experienced testers, or multiple perspectives through pair testing approaches.
Risk-based planning also involves regular reassessment as projects evolve. New features, changing requirements, and discovered issues may shift risk profiles, requiring adjustments to exploratory testing strategies. This adaptive approach ensures that testing efforts remain aligned with project priorities throughout development cycles.
Time-Boxing and Session Management
Effective time management is crucial for exploratory test management success. Time-boxing creates urgency that helps testers maintain focus while preventing sessions from becoming unfocused or inefficient. Most teams find that 60-120 minute sessions provide optimal balance between depth and sustained attention.
Session management involves more than just time limits. Effective approaches include pre-session preparation where testers review charters and gather necessary resources, focused execution periods with minimal interruptions, and post-session analysis where findings are documented and reviewed.
Many teams implement session tracking tools that help manage schedules, assign testers to specific charters, and monitor overall coverage across different application areas. This systematic approach ensures that exploratory efforts remain coordinated and comprehensive rather than random or duplicative.
Cross-Team Collaboration
Exploratory test management succeeds when it involves multiple perspectives and expertise areas. Developers bring technical knowledge about system architecture and potential failure points, while product owners contribute business context and user perspective. This collaborative approach enriches exploratory efforts and ensures comprehensive coverage.
Collaborative approaches might include pair testing sessions where testers work with developers or product owners, group brainstorming sessions to develop test charters, or cross-functional debriefing meetings where findings are analyzed from multiple perspectives.
Tools that support collaboration become essential for distributed teams. Shared documentation systems, real-time communication platforms, and integrated test management solutions enable effective collaboration regardless of physical location.
What Are the Common Challenges and How Do You Solve Them?
While structured exploratory testing offers significant advantages, implementation often encounters predictable obstacles that can undermine success if not addressed proactively. Understanding these challenges and their proven solutions helps teams avoid common pitfalls and accelerate their path to effective exploratory testing practices.
How Do You Handle Documentation and Traceability Issues?
One of the most significant challenges in exploratory testing is maintaining adequate documentation without disrupting the investigative flow. Traditional approaches often resulted in poor documentation that made it difficult to reproduce issues or build upon previous discoveries.
Modern solutions address this challenge through multiple approaches including lightweight documentation templates, collaborative testing tools, and post-session structured debriefing processes. The key is finding the right balance between capture thoroughness and testing efficiency.
For example, platforms like TestQuality provide integrated session management capabilities that enable testers to capture findings without disrupting their investigative flow, with development tool integrations ensuring discoveries are immediately accessible to relevant team members.
Resource Allocation and Scaling
Many organizations struggle with allocating appropriate resources to exploratory testing, particularly when facing tight deadlines or resource constraints. The perceived "unstructured" nature of exploratory testing sometimes leads to under-investment compared to scripted testing approaches.
Successful organizations address these challenges by demonstrating clear ROI from exploratory efforts through metrics such as defect discovery rates, customer satisfaction improvements, and reduced production issues. They also implement structured approaches that make exploratory testing more predictable and manageable.
Scaling exploratory efforts requires systematic approaches including standardized charter templates, consistent documentation practices, and effective knowledge sharing mechanisms. Organizations that successfully scale exploratory testing typically invest in tools and processes that support coordination across multiple testers and projects.
Integration with Existing Workflows
Integrating structured exploratory testing with existing development and QA processes requires careful planning and change management. Teams accustomed to highly structured testing approaches may initially resist the flexibility inherent in exploratory methods.
Successful integration typically involves gradual implementation starting with pilot projects or specific application areas. This approach allows teams to develop expertise and demonstrate value before expanding exploratory approaches more broadly.
Modern test management platforms facilitate integration by providing seamless connections between exploratory sessions and formal test plans, defect tracking systems, and reporting tools. This integration ensures that exploratory findings contribute to overall quality metrics and decision-making processes.
7 Essential Techniques for Exploratory Test Management
1. User Story-Based Exploration
User story-based exploration aligns exploratory testing efforts with business value and user needs. This approach uses user stories as starting points for exploratory sessions, ensuring that testing efforts focus on functionality that matters most to end users.
Effective user story exploration involves creating realistic user personas and scenarios, then following the natural flow of user interactions while remaining alert for unexpected behaviors or edge cases. This approach often reveals usability issues and integration problems that formal test cases might miss.
Teams implementing user story-based exploration often discover discrepancies between intended user workflows and actual system behavior. These insights prove valuable for both quality assurance and product development, leading to improved user experiences and more intuitive software designs.
2. Error Guessing and Boundary Testing
Experienced testers develop intuition about where software is likely to fail based on common failure patterns, system architecture, and previous experience. Error guessing leverages this expertise to focus exploratory efforts on areas most likely to contain defects.
Boundary testing within exploratory sessions involves investigating system behavior at the edges of expected input ranges, capacity limits, and operational parameters. This approach often uncovers critical issues related to system stability, performance, and error handling.
Combining error guessing with systematic boundary exploration creates powerful testing strategies that efficiently identify high-impact issues. Testers learn to recognize patterns and develop increasingly sophisticated intuition about potential failure points.
3. Tours-Based Testing Approaches
Tours-based testing provides structured approaches to exploratory sessions while maintaining investigative flexibility. Different "tours" focus on specific aspects of the application such as functionality, user experience, or technical implementation.
The "guidebook tour" approach involves exploring the application as a new user would, following documentation and help systems to understand intended workflows. The "money tour" focuses on revenue-critical features and transactions. The "stress tour" deliberately pushes system limits to identify breaking points.
Tours provide excellent frameworks for organizing exploratory efforts across teams and ensuring comprehensive coverage of different application aspects. Many teams develop custom tours based on their specific application characteristics and business priorities.
4. Session-Based Charter Development
Effective charter development creates focused missions for exploratory sessions without constraining creativity. Strong charters include clear objectives, specific areas to investigate, and realistic time boundaries while leaving room for serendipitous discoveries.
Charter creation should involve collaboration between testers, developers, and product owners to ensure alignment with business priorities and technical realities. Regular charter review helps teams refine their approach and improve session effectiveness over time.
5. Pair Testing Methodologies
Pair testing combines different perspectives and expertise areas to enhance exploratory effectiveness. Two testers working together can cover more ground, catch issues that individuals might miss, and create comprehensive documentation through shared observation.
Effective pair testing involves clearly defined roles such as navigator and driver, regular switching of responsibilities, and structured debriefing to capture insights from both participants. This collaborative approach also facilitates knowledge transfer and skill development.
6. Risk-Based Exploration Prioritization
Strategic risk assessment guides exploratory efforts toward areas most likely to contain critical issues or business-impacting defects. This prioritization ensures efficient use of testing resources while maximizing the value of discoveries.
Risk-based prioritization considers factors such as business criticality, technical complexity, recent changes, and historical defect patterns. Regular reassessment helps teams adapt their focus as projects evolve and new information becomes available.
7. Documentation and Knowledge Capture Systems
Systematic documentation transforms individual discoveries into team knowledge that can guide future testing efforts. Effective documentation captures not only defects but also insights about user experience, system behavior, and areas requiring additional investigation.
Modern documentation approaches leverage multimedia capture, collaborative tools, and integration with development workflows to ensure that insights are preserved and accessible. The goal is creating searchable knowledge repositories that enhance team capability over time.
What Tools and Technologies Support Modern Exploratory QA?
The right technology stack can dramatically enhance the effectiveness of structured exploratory testing by providing frameworks for session planning, comprehensive documentation capabilities, and seamless integration with existing development workflows. Modern exploratory testing success depends on selecting tools that balance structure with flexibility.
How Do You Choose Session Management Platforms?
Modern exploratory test management requires tools that support session planning, execution tracking, and results analysis. Effective platforms provide charter management, time tracking, note-taking capabilities, and integration with broader development workflows.
Leading session management tools offer features such as automated session scheduling, collaborative note-taking, screenshot and screen recording capabilities, and integration with defect tracking systems. These capabilities transform exploratory testing from individual activities into coordinated team efforts.
The choice of session management platform depends on team size, integration requirements, and collaboration needs. Organizations should evaluate platforms based on ease of use, integration capabilities, reporting features, and scalability to future needs.
Documentation and Collaboration Tools
Effective documentation tools for exploratory testing must balance thoroughness with efficiency. Modern solutions provide templates, multimedia capture capabilities, and integration with knowledge management systems to ensure that insights are preserved and accessible.
Collaboration tools become essential for distributed teams or complex projects involving multiple testers. Real-time sharing capabilities, commenting systems, and version control help coordinate efforts and prevent duplication while enabling knowledge sharing across team members.
Cloud-based platforms offer particular advantages for exploratory testing documentation by providing access from any device and enabling real-time collaboration. These platforms also typically offer better integration with development tools and CI/CD pipelines.
Integration with Test Management Systems
Modern platforms require seamless integration with broader test management ecosystems including test case management, defect tracking, and requirement traceability systems. This integration ensures that exploratory findings contribute to overall quality metrics and decision-making.
Integration capabilities should include automated defect creation from exploratory findings, linking between exploratory sessions and related test cases, and comprehensive reporting that combines insights from all testing approaches. This holistic view enables better decision-making about software quality and release readiness.
Unified platforms support this by merging exploratory sessions with scripted test cases in a single workflow. For teams practicing BDD, this might include Gherkin scenario generation from exploratory notes—bridging the gap between structured and ad-hoc testing.
How Do You Implement Best Practices for Team Success?
Successful structured exploratory testing implementation depends on more than just processes and tools—it requires developing team capabilities, establishing meaningful metrics, and creating continuous improvement frameworks. Organizations that invest in these foundational elements see significantly better outcomes from their exploratory testing programs.
Training and Skill Development
Successful exploratory testing requires specific skills that differ from traditional scripted testing approaches. Teams need training in session management, charter development, effective documentation practices, and collaborative testing techniques.
Training programs should combine theoretical understanding with practical exercises using real applications. Hands-on practice helps testers develop the investigative mindset and systematic approaches that make exploratory testing effective.
Ongoing skill development involves regular practice, peer learning opportunities, and exposure to different testing contexts. Many organizations implement mentorship programs where experienced exploratory testers guide newcomers through increasingly complex scenarios.
Quality Metrics and Measurement
Measuring the effectiveness of structured exploratory testing requires metrics that capture both quantitative and qualitative aspects of testing efforts. Traditional metrics such as test case execution counts don't apply directly to exploratory approaches.
Effective metrics for exploratory testing include defect discovery rates, coverage assessments based on charter completion, session productivity measures, and qualitative assessments of findings importance. These metrics help teams optimize their exploratory approaches and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
Long-term success measurement should focus on outcomes such as reduced production defects, improved customer satisfaction, and decreased time-to-market. These business-level metrics help justify investment in exploratory testing capabilities and guide strategic decisions about testing approaches.
Continuous Improvement Processes
Structured exploratory approaches benefit from regular retrospectives and process improvement efforts. Teams should regularly assess the effectiveness of their charter development, session management, and documentation practices.
Improvement processes might involve analyzing patterns in discovered defects to identify areas requiring more exploratory attention, adjusting session lengths based on productivity assessments, or modifying documentation approaches based on usage patterns.
Successful teams also learn from external sources including industry best practices, tool improvements, and research findings. Staying current with evolving exploratory testing techniques helps teams maintain competitive advantages and avoid stagnation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between exploratory testing and exploratory test management?
Exploratory testing refers to the investigative testing approach itself, while structured exploratory testing encompasses the systematic processes, tools, and strategies used to organize, execute, and leverage exploratory testing within broader quality assurance frameworks. The management aspect adds structure, documentation, and integration capabilities to traditional exploratory approaches.
How do you measure ROI from structured exploratory testing initiatives?
ROI measurement combines quantitative metrics such as defect discovery rates, reduced production issues, and decreased debugging time with qualitative benefits including improved user experience and better product-market fit. Many organizations track the cost of defects found through structured exploratory testing versus the cost of addressing the same issues in production.
Can structured exploratory testing work with automated testing strategies?
Absolutely. Modern QA strategies use exploratory and automated testing as complementary approaches. Automated testing handles repetitive scenarios and regression testing while structured exploratory sessions investigate new functionality, edge cases, and user experience concerns. The combination provides more comprehensive coverage than either approach alone.
What skills do testers need for effective structured exploratory testing?
Key skills include investigative thinking, systematic documentation practices, effective communication for findings sharing, basic understanding of software architecture, and familiarity with session management techniques. Domain expertise in the application area being tested also significantly enhances exploratory testing effectiveness.
How long should exploratory testing sessions last?
Most teams find that 60-120 minute sessions provide optimal balance between focus and thoroughness. Shorter sessions may not allow sufficient depth while longer sessions often lead to decreased attention and productivity. The specific duration should be adjusted based on session complexity, tester experience, and application characteristics.
Conclusion: Transform Your QA Strategy with Strategic Exploratory Test Management
Structured exploratory testing represents the evolution of quality assurance from rigid, script-driven processes to adaptive, intelligence-driven approaches that leverage human creativity while maintaining systematic rigor. As software development continues accelerating and user expectations rise, organizations need testing strategies that combine thoroughness with flexibility.
The most successful QA teams recognize that this approach isn't a replacement for other testing methods but rather a crucial complement that addresses gaps in automated and scripted testing. By implementing systematic exploratory approaches, teams can uncover critical issues, improve user experience, and deliver higher-quality software more efficiently.
Ready to transform your quality assurance strategy with comprehensive structured exploratory testing capabilities? Start your free trial with TestQuality and discover how integrated test management platforms can elevate your testing effectiveness while streamlining your development workflows.