Key Takeaways:
The testing landscape has evolved significantly, and choosing between Selenium and Cucumber isn't always an either-or decision in 2025.
- Selenium excels at browser automation and technical testing scenarios requiring precise UI interaction control
- Cucumber bridges the gap between business requirements and technical implementation through natural language testing
- Modern teams often integrate both tools to maximize collaboration while maintaining robust automation capabilities
- A unified test management approach, such as that offered by TestQuality, can eliminate the complexity of managing separate toolsets, providing a central hub for all testing activities
The most effective testing strategies in 2025 combine both tools' strengths rather than forcing teams to choose sides.
The eternal debate between Selenium vs Cucumber continues to challenge testing teams in 2025, but the reality is more nuanced than choosing one over the other. According to industry research, 72.3% of teams are actively exploring or adopting AI-driven testing workflows, while 33% of companies seek to automate between 50% to 75% of their testing process, suggesting that the future belongs to integrated approaches rather than single-tool solutions.
Testing teams face mounting pressure to deliver faster while maintaining quality. Selenium and Cucumber each solve different pieces of this puzzle. Selenium provides powerful browser automation capabilities that technical teams love, while Cucumber enables behavior-driven development that keeps business stakeholders engaged and aligned with development goals.
The selenium vs cucumber choice isn't just about technical capabilities—it's about how your team works, communicates, and delivers value. Recent industry analysis shows that 77% of organizations are now investing in AI to optimize quality assurance processes, highlighting the evolution toward more sophisticated testing strategies that often combine multiple approaches.
What Is Selenium vs Cucumber in 2025?
Understanding the fundamental differences between these tools requires looking beyond surface-level comparisons. While both serve the testing ecosystem, they operate at entirely different levels of the automation stack.
Selenium functions as a comprehensive browser automation framework, providing direct control over web elements, user interactions, and browser behavior. It's the engine that powers millions of automated tests worldwide, offering precise control over every aspect of web application testing.
Cucumber operates as a behavior-driven development tool that translates human-readable requirements into executable tests. It doesn't compete with Selenium; instead, it often orchestrates Selenium-powered tests through natural language scenarios that anyone can understand.
Modern Testing Architecture: Where Each Tool Fits
The 2025 testing landscape has moved beyond simple tool comparisons toward architectural thinking. Modern testing frameworks often feature multiple layers where different tools excel at specific functions.
At the execution layer, Selenium provides unmatched browser automation capabilities. Its WebDriver protocol has become the industry standard, supported by all major browsers and integrated into countless CI/CD pipelines. Teams use Selenium when they need precise control over web interactions, complex test data management, or integration with existing technical infrastructure.
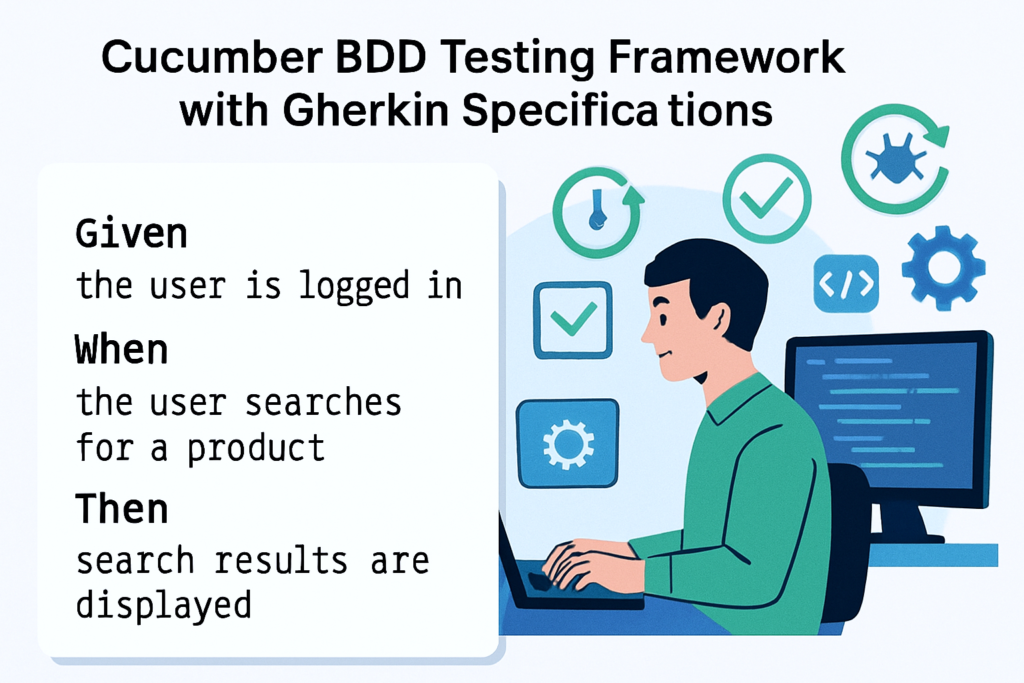
At the specification layer, Cucumber excels at translating business requirements into testable scenarios. Its Gherkin syntax creates a shared language between stakeholders, making requirements tangible and testable. This approach has proven particularly valuable in agile environments where requirements evolve rapidly and stakeholder alignment is critical.
Understanding the selenium vs cucumber comparison requires recognizing that these tools operate at different abstraction levels, serving complementary rather than competing purposes in modern testing workflows.
Core Differences: Selenium vs Cucumber Analysis
The technical distinctions between Selenium and Cucumber reflect their different purposes within the testing ecosystem. These differences determine when teams should choose one approach over another, or how to combine them effectively.
Technical Architecture and Implementation
Selenium operates at the browser level, communicating directly with web drivers to control browser behavior. This direct access provides complete control over timing, element interaction, and browser state management. Teams can implement complex testing scenarios, handle dynamic content, and integrate with various programming languages including Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript.
Cucumber functions as a testing orchestrator, using step definitions to connect natural language scenarios with underlying automation code. When teams combine Cucumber with Selenium, Cucumber handles the test specification while Selenium manages the actual browser automation. This separation creates maintainable test suites that remain accessible to non-technical stakeholders.
Programming Language Support and Flexibility
Selenium's multi-language support makes it adaptable to virtually any development environment. Teams can write tests in their preferred programming language while maintaining consistency with their existing codebase. This flexibility has made Selenium the foundation for countless custom testing frameworks.
Cucumber supports multiple programming languages but requires additional setup for each implementation. The Gherkin syntax remains consistent across languages, but teams must maintain step definitions in their chosen programming environment. This dual-language approach can add complexity but also creates clear separation between test specifications and implementation details.
When to Choose Selenium for Your Testing Strategy
Selenium becomes the clear choice when teams need maximum control over test execution, complex browser interactions, or integration with existing technical workflows. Several scenarios strongly favor Selenium's direct approach to browser automation.
Technical Testing Requirements
Teams working with complex web applications often require fine-grained control over test execution. Selenium excels when tests must handle dynamic content, complex user workflows, or precise timing requirements. For example, testing real-time applications like trading platforms or collaborative tools requires the exact timing control that Selenium provides.
Advanced testing scenarios such as cross-browser compatibility testing, performance testing, or integration with existing CI/CD pipelines also favor Selenium's technical approach. Teams can build sophisticated test frameworks that handle data-driven testing, parallel execution, and custom reporting without additional abstraction layers.
Development Team Structure Considerations
Organizations with primarily technical testing teams often find Selenium's direct approach more efficient. When QA engineers have strong programming backgrounds and work closely with development teams, Selenium's flexibility outweighs the collaboration benefits of natural language testing.
Selenium also fits naturally into development workflows where tests are written and maintained by the same teams building the application. This alignment reduces communication overhead and allows for rapid test development and maintenance. Industry research shows that teams report automation testing effectively enhances productivity and reduces costs when implemented with appropriate technical expertise.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Tool Selection
The selenium vs cucumber decision often comes down to resource allocation and long-term maintenance costs. Selenium requires higher upfront investment in technical skills but can deliver faster execution and simpler maintenance for teams with appropriate expertise. Organizations implementing comprehensive automation strategies see testing costs reduced while product quality improves.
Cucumber's business stakeholder engagement benefits become crucial when requirements change frequently or when testing must align closely with business processes. The natural language approach can reduce requirement clarification cycles and significantly accelerate development timelines through improved stakeholder communication.
Platforms like TestQuality are designed to provide a cohesive environment for both Selenium and Cucumber workflows, ensuring consistent reporting and improved team collaboration across diverse testing strategies.
When Cucumber Transforms Your Testing Approach
Cucumber shines when teams prioritize collaboration, requirement clarity, and stakeholder engagement over pure technical control. The tool's behavior-driven development approach fundamentally changes how teams think about testing and requirements management.
Business Stakeholder Engagement
Organizations where business analysts, product owners, or domain experts actively participate in defining requirements find Cucumber invaluable. The natural language syntax allows these stakeholders to write, review, and understand test scenarios without technical expertise.
This collaboration often reveals requirement gaps or ambiguities before development begins, reducing expensive late-stage changes. Teams report that Cucumber scenarios frequently expose edge cases that purely technical testing approaches might miss.
Research from leading academic institutions shows that BDD facilitates collaboration between stakeholders and helps improve cooperation in large-scale projects. This improvement stems from the collaborative requirement definition process that BDD naturally enforces, creating shared understanding across technical and business teams.
Requirement Traceability and Documentation
Cucumber scenarios serve as living documentation that evolves with the application. Unlike traditional requirements documents that quickly become outdated, Cucumber scenarios remain current because they're part of the active test suite.
This approach creates seamless traceability from business requirements through test implementation to execution results. Teams can demonstrate feature coverage, track requirement changes, and communicate testing status using the same artifacts that define the tests themselves.
The selenium vs cucumber debate often centers on documentation value. While Selenium tests document technical implementation details, Cucumber scenarios document business intent and user value, providing different but equally important perspectives on system behavior.
Essential Technical Comparison: Feature-by-Feature Analysis
Understanding the specific capabilities and limitations of each tool helps teams make informed decisions about their testing architecture. This detailed comparison reveals where each tool excels and where compromises may be necessary.
| Feature Category | Selenium | Cucumber | Integration Approach |
| Browser Control | Direct WebDriver API access | Requires underlying automation tool | Cucumber orchestrates Selenium commands |
| Language Support | Java, Python, C#, JavaScript, Ruby | Gherkin + programming language for steps | Combined approach uses both |
| Learning Curve | Steep for non-programmers | Gentle for business users | Gradual team adoption possible |
| Test Maintenance | Code-level changes required | Natural language updates | Dual-layer maintenance strategy |
| Execution Speed | Optimized for performance | Additional interpretation layer | Balanced approach with selective automation |
| Debugging | Standard programming tools | Limited debugging options | Hybrid debugging strategies |
| Reporting | Custom or framework-based | Business-readable reports | Unified reporting across tools |
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Selenium's direct approach typically delivers faster execution times, making it ideal for large test suites or performance-critical scenarios. Teams running thousands of tests daily often prefer Selenium's efficiency over Cucumber's interpretive overhead.
However, Cucumber's natural language approach can accelerate test creation and maintenance when business requirements change frequently. Teams find that the initial investment in Cucumber framework setup pays dividends in long-term maintainability and stakeholder engagement.
Industry research indicates that the automation testing market is growing at 17% CAGR, driven by organizations seeking both technical efficiency and business alignment. This growth reflects teams choosing tools based on specific organizational needs rather than one-size-fits-all approaches.
This trend underscores the value of integrated platforms, where TestQuality helps bridge the gap between technical execution (like Selenium) and business-driven specifications (like Cucumber), catering to diverse organizational needs within a single, streamlined environment.
Real-World Implementation Success Stories
Modern organizations have developed sophisticated approaches to the selenium vs cucumber question that go beyond simple tool selection. These success stories demonstrate how strategic thinking about testing architecture can deliver better outcomes than tool-focused decisions.
Enterprise-Scale BDD Implementation
A major financial services company implemented a hybrid approach where critical user journeys are specified in Cucumber for regulatory compliance and stakeholder communication, while technical integration tests use pure Selenium for efficiency. This approach demonstrates how different test scenarios serve different organizational needs.
The key insight was recognizing that customer-facing features benefit from Cucumber's stakeholder engagement, while backend integration testing leverages Selenium's technical precision.
Agile Development Team Transformation
A software product company transformed their testing approach by implementing Cucumber for sprint planning and Selenium for continuous integration. Product owners write acceptance criteria as Cucumber scenarios during sprint planning, while developers implement technical tests in Selenium for automated pipeline execution.
This selenium vs cucumber integration demonstrates the value of behavior-driven development in facilitating stakeholder collaboration while maintaining robust automated testing coverage.
Tools like TestQuality further enhance this synergy by providing a centralized hub for managing both BDD scenarios and Selenium test results, ensuring complete traceability and visibility for all team members.
Integration Strategies: Combining Selenium and Cucumber
Modern testing strategies often leverage both tools' strengths through thoughtful integration approaches. Rather than choosing between them, sophisticated testing teams design architectures that utilize each tool where it provides maximum value.
Layered Testing Architecture
Successful integration typically involves a layered approach where Cucumber handles test specification and Selenium manages execution. This separation allows business stakeholders to define requirements in natural language while technical teams implement robust automation underneath.
Teams often structure their integration with Cucumber feature files defining high-level scenarios, step definitions translating those scenarios into technical actions, and Selenium providing the actual browser automation. This approach maintains clear separation of concerns while delivering both collaboration benefits and technical control.
A robust test management platform like TestQuality can be instrumental in maintaining this separation of concerns, offering clear dashboards and reporting that reflect both the BDD layer and the underlying automation results.
Hybrid Implementation Strategies
Organizations frequently implement hybrid approaches where different types of tests use different tools. Critical user journeys might be specified in Cucumber for stakeholder clarity, while detailed technical tests use pure Selenium for efficiency.
This selective approach allows teams to optimize for different goals within the same project. Behavior-driven development scenarios can focus on user value while technical regression tests ensure system stability.
Modern Development Workflow Integration
The 2025 testing landscape emphasizes continuous integration, rapid feedback loops, and seamless tool integration. Both Selenium and Cucumber have evolved to support modern development practices, but with different strengths and approaches.
CI/CD Pipeline Considerations
Selenium's mature ecosystem provides extensive CI/CD integration options. Teams can easily incorporate Selenium tests into Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Azure DevOps pipelines with minimal configuration. The tool's stability and performance make it ideal for automated pipeline execution.
When integrating Cucumber, robust reporting and clear stakeholder communication are crucial. Platforms like TestQuality are designed to consolidate reports from both Selenium and Cucumber, generating business-readable dashboards that facilitate shared understanding and streamlined communication across the entire CI/CD pipeline.
DevOps and Monitoring Integration
Modern testing extends beyond simple pass/fail results to include performance monitoring, user experience tracking, and business metric validation. Selenium's flexibility allows integration with monitoring tools, performance testing platforms, and custom analytics solutions.
TestQuality complements this by providing a centralized repository for all test results, enabling teams to correlate performance metrics, user experience data, and business metrics directly with test outcomes, thus supporting a holistic DevOps approach.
Cucumber's business-focused approach aligns naturally with feature flagging, A/B testing, and user behavior analysis. Teams can link test scenarios directly to business metrics, creating closed-loop feedback systems between testing and product management.
Advanced Use Cases and Implementation Patterns
Sophisticated testing teams have developed advanced patterns that maximize the value of both tools while minimizing their individual limitations. These approaches represent the current state of the art in automated testing strategy.
Microservices and API Testing Integration
Modern applications often combine web interfaces with complex API ecosystems. Teams use Selenium for user interface testing while integrating API testing directly into Cucumber scenarios. This approach provides end-to-end validation that covers both user interactions and underlying service behavior.
For example, a Cucumber scenario might verify that user actions trigger appropriate API calls, data updates occur correctly, and the interface reflects changes accurately. This comprehensive approach catches integration issues that pure UI or API testing might miss.
Cloud-Native Testing Strategies
Cloud deployment has changed testing requirements, emphasizing scalability, environment consistency, and rapid provisioning. Selenium's cloud integrations allow teams to run tests across multiple browser versions and operating systems without maintaining local infrastructure.
Cucumber scenarios can specify environment-agnostic requirements that execute consistently across development, staging, and production environments. This consistency helps teams maintain confidence in their deployment pipeline while reducing environment-specific testing overhead.
Leading organizations are implementing containerized testing approaches where Cucumber scenarios drive Selenium tests in Docker containers, enabling both collaboration benefits and scalable execution. This architecture supports modern DevOps practices while maintaining the flexibility to choose the best tool for each testing scenario.
TestQuality provides a unified command and control center for these containerized environments, allowing teams to manage and monitor tests running across diverse cloud-native setups, ensuring consistent execution and reporting.
Strategic Decision Framework for Tool Selection
Rather than viewing selenium vs cucumber as a binary choice, successful organizations develop decision frameworks that optimize tool selection based on specific project characteristics and organizational constraints.
Team Capability Assessment
The first consideration involves honestly assessing team technical capabilities and stakeholder engagement requirements. Organizations with strong technical teams and limited business stakeholder involvement often benefit from Selenium's direct approach, while teams requiring frequent stakeholder collaboration find Cucumber's natural language approach invaluable.
Consider factors like programmer-to-tester ratios, business analyst involvement in testing, and regulatory or compliance requirements that might mandate certain documentation approaches. Teams with limited programming resources might find Cucumber's accessibility enables broader participation in test creation and maintenance.
Academic research confirms that BDD facilitates interaction between many stakeholders in large-scale software projects, making it particularly valuable for complex organizational environments requiring extensive collaboration.
Project Complexity and Timeline Considerations
Simple applications with straightforward user interactions often benefit from Selenium's directness, while complex business applications with intricate workflows might require Cucumber's requirement clarity and stakeholder engagement capabilities.
Timeline pressures also influence tool selection. Teams facing aggressive delivery schedules might prefer Selenium's faster implementation for technical users, while projects requiring extensive stakeholder buy-in benefit from Cucumber's collaborative approach despite longer initial setup times.
Test Maintenance and Long-term Strategy
Choosing between Selenium and Cucumber significantly impacts long-term test maintenance costs and effectiveness. Understanding these implications helps teams make strategic decisions that will serve them well as their applications and testing needs evolve.
Maintenance Complexity and Resource Requirements
Selenium tests require ongoing maintenance by technically skilled team members. As applications evolve, tests must be updated at the code level, requiring programming expertise and understanding of both the testing framework and the application under test.
Cucumber's natural language approach can simplify maintenance for certain types of changes. When business logic evolves but technical implementation remains stable, teams can update Cucumber scenarios without modifying underlying step definitions. However, significant application changes still require technical updates to step definitions and Selenium integration code.
Scaling Testing Teams and Knowledge Transfer
Organizations planning to scale their testing efforts must consider how tool choice affects team growth and knowledge transfer. Selenium's technical requirements mean new team members need programming skills and framework-specific training.
Cucumber's approachable syntax allows business stakeholders and junior team members to contribute to test creation and maintenance. This accessibility can accelerate team scaling and reduce dependence on senior technical resources for routine test maintenance.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Teams implementing either Selenium or Cucumber often encounter predictable challenges that can derail testing initiatives. Understanding these pitfalls and their solutions helps teams achieve success more quickly and avoid expensive mistakes.
Over-Engineering vs Under-Engineering
Selenium's flexibility can lead teams to build overly complex testing frameworks that become maintenance burdens. Teams should resist the temptation to solve every possible testing problem upfront and instead focus on delivering value incrementally.
Cucumber implementations can suffer from the opposite problem, where teams underestimate the technical complexity required for robust step definitions. Successful Cucumber implementations require significant upfront investment in framework design and step definition architecture.
Stakeholder Engagement and Expectation Management
Cucumber's promise of business stakeholder involvement often falls short when teams don't invest in proper training and engagement processes. Business users won't automatically adopt natural language testing without support, training, and clear value demonstration.
Selenium projects can fail when teams don't communicate testing progress and results effectively to non-technical stakeholders. Technical testing approaches require additional effort to translate results into business-relevant information.
Future-Proofing Your Testing Strategy
The testing landscape continues evolving rapidly, with new tools, approaches, and requirements emerging regularly. Making strategic decisions that remain valuable over time requires understanding current trends and likely future developments.
Emerging Testing Paradigms
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to impact automated testing through intelligent test generation, self-healing tests, and predictive failure analysis. Both Selenium and Cucumber can benefit from these advances, but in different ways.
Selenium's programmatic approach aligns naturally with AI-powered test optimization and maintenance tools. Teams can leverage machine learning to improve test reliability, reduce maintenance overhead, and optimize execution strategies.
Cucumber's natural language foundation makes it an ideal candidate for AI-powered test generation from requirements documents, user stories, or even recorded user sessions. Future developments may allow teams to generate comprehensive test suites directly from business requirements.
Integration with Modern Development Practices
The shift toward shift-left testing, continuous deployment, and feature flagging creates new requirements for testing tools. Teams need rapid feedback, fine-grained control over test execution, and seamless integration with deployment pipelines.
Both Selenium and Cucumber are evolving to support these practices, but teams must choose implementations that align with their specific development workflow requirements. The tools that integrate most seamlessly with existing development practices will provide the greatest long-term value.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Selenium and Cucumber be used together in the same project? Yes, many successful testing strategies combine both tools. Cucumber can orchestrate Selenium-powered tests, providing natural language scenarios that execute through Selenium's browser automation capabilities. This integration offers the collaboration benefits of Cucumber with the technical control of Selenium. TestQuality enhances this combined approach by providing a central platform to manage these integrated tests, offering a clear view of both BDD scenarios and detailed Selenium execution results, thus maximizing the benefits of both tools.
Which tool is better for teams with limited programming experience? Cucumber is generally more accessible for teams with limited programming experience, as its Gherkin syntax uses natural language that business stakeholders can read and write. However, implementing the underlying step definitions still requires programming skills, so teams typically need at least some technical expertise.
How do maintenance costs compare between Selenium and Cucumber approaches? Maintenance costs depend heavily on team structure and application characteristics. Pure Selenium implementations may require less overhead for simple test updates but need technical skills for all changes. Cucumber adds complexity through its dual-layer architecture but can simplify maintenance when business logic changes frequently while technical implementation remains stable.
What's the performance difference between Selenium and Cucumber test execution? Selenium typically executes faster since it communicates directly with browsers without additional interpretation layers. Cucumber adds overhead through its scenario parsing and step definition matching, but the difference is usually negligible for most testing scenarios. Teams with thousands of tests might notice performance differences, but most projects won't be significantly impacted.
Which approach better supports CI/CD integration? Both tools integrate well with modern CI/CD pipelines, but in different ways. Selenium offers more direct integration options and typically faster execution suitable for automated pipelines. Cucumber provides more business-readable reports that can be valuable for stakeholder communication, but may require additional configuration for optimal pipeline integration.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Path Forward

The Selenium vs Cucumber decision ultimately depends on your team's specific context, goals, and constraints rather than abstract tool capabilities. Successful testing strategies align tool choice with organizational realities including team skills, stakeholder engagement requirements, and long-term maintenance capabilities.
Teams with strong technical capabilities and established development processes often find Selenium's direct approach more efficient and maintainable. Organizations prioritizing stakeholder collaboration and requirement clarity typically benefit more from Cucumber's behavior-driven development approach.
"The most successful testing strategies in 2025 often involve thoughtful integration of multiple tools rather than commitment to a single approach. To avoid wrestling with complex tool integrations and management overhead, discover how TestQuality provides unified test management that seamlessly works with both Selenium and Cucumber workflows. Visit TestQuality.com today to learn more about how a truly integrated platform can eliminate testing complexity, streamline collaboration, and help your team deliver higher quality software faster."