From NoSuchElementException and ElementNotVisibleException to StaleElementReferenceException and TimeOutException, each exception highlights unique issues that can occur during test execution. Understanding these common WebDriver exceptions, such as NoSuchFrameException, NoSuchAlertException, and InvalidSelectorException, is crucial for crafting more reliable test scripts.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the most frequently encountered WebDriver exceptions, explain their causes, and provide practical tips to handle them effectively—ensuring your Selenium tests run smoothly.
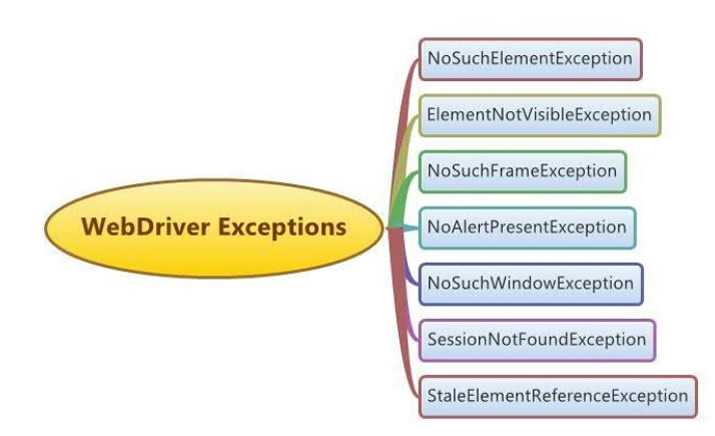
Developers and Testers use an exception handling framework to handle an exception in selenium scripts. The below diagram depicts the different types of Exceptions that we commonly face while working with Selenium WebDriver:
Before understanding the different types of Exceptions that we may face while working with Selenium WebDriver, first I will explain the term Exception.
What is an Exception ?
Exception is a problem that occurs during the execution of the program and when an Exception occurs the program execution will stop and the rest of the code in the program will not be executed.
Exceptions must be handled because they disrupt the usual flow of a program's execution. One of the primary goals of exception handling is to prevent this break and keep the application running. On the occurrence of a certain exception, you may wish to do a set of actions.
There are three kinds of exceptions in Selenium and Java:
- Checked Exception: Checked exceptions are handled during compile time, and if they are not caught and handled during compile time, they cause a compilation problem.
- Unchecked Exception: A compiler does not need handling of unchecked exceptions. During compilation, the compiler ignores it.
- Error: When a scenario becomes fatal and the software is unable to recover
Example for Exception:
Let's say, we have 5 lines in our Program as shown below and if an exception occurs at the 3rd line, the program execution will stop and the remaining lines i.e. 4th and 5th in our program won't be executed.Statement1;
Statement2;
Statement3; //Exception occurred at this 3rd line
Statement4; //This line wont be executed
Statement5; //This line wont be executed
Example of an Exception in Java:
Java Program Code:
Read the comments in the below Java program code:
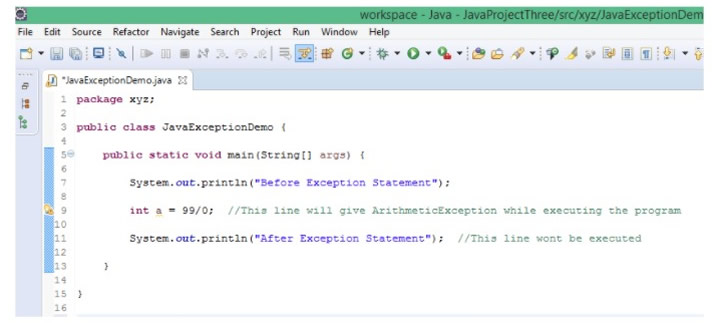
Output:
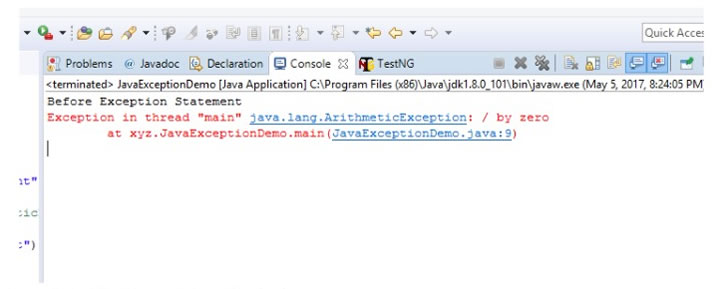
The below output will be displayed in the Eclipse IDE console. From the output, it's very clear that the Program execution stopped due to ArithmeticException and the last statement in the above program didn’t get executed:
Example for Handling an Exception in Java:
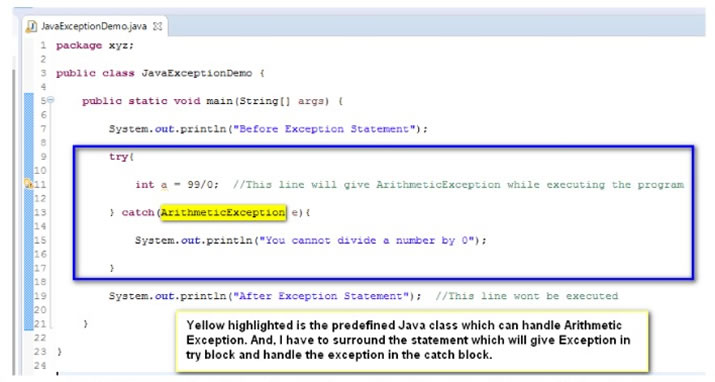
In the above program, if we want to continue the execution of the Java program, even after the exception occurs, we have to handle it. The method of handling the exception is known as Exceptional Handling. Surround the Java Statement which is throwing the Exception using the ‘try … catch’ block as shown in the below screenshot:
Note: catch block in ‘try .. catch’ will use the respective Class which is required to handle the Exception. Since the exception thrown in the above program is ArithmeticException, we have a predefined class in Java known as ArithmeticException which can handle this exception.
Now, execute the Exception handled code and observe that Exception will be handled and program will continue to execute without stopping when the exception occurs. The below output displayed in the Eclipse IDE console is the proof that the exception got handled and the program continued to execute:
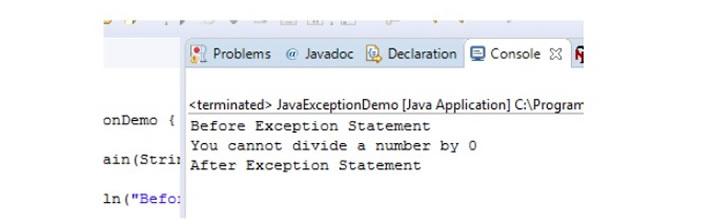

If you still want to understand Exceptions and their handling mechanism in a detailed manner, you can go through the following posts:
- Exceptional Handling
- What happens when we don't handle an Exception
- How to handle an Exception
- Exception Hierarchy
- Catching Exceptions using Throwable Class
- Catching Exceptions using Exception Class
- Catching arithmetic exception using ArithmeticException Class
- Handling ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- Using multiple catch blocks
- Order of catch blocks
- Handling exceptions using Exception Class for safe side
- Methods of Throwable Class
- Printing the exception details in different ways
- Using getMessage() of Throwable Class
- Using toString() of Throwable Class
- Using printStackTrace() of Throwable Class
- Using the throw keyword in Exception Handling
- Checked Exceptions
- Using throws in exception handling
- Handling FileNotFoundException
- Using Finally in exception handling
- Using the finally block immediately after the try block
- Nested try-catch blocks
- Catching Multiple Exceptions in a single catch block
Different types of Exceptions in Selenium WebDriver
From the above examples, you understand what is an Exception and what happens when it occurs during program execution. Now, I will explain all the different types of Exceptions, we may face while working with Selenium WebDriver.Though there are many WebDriver Exceptions in Selenium, below are the different WebDriver Exceptions that we commonly face while working with Selenium:
- NoSuchElementException
- ElementNotVisibleException
- NoSuchFrameException
- NoAlertPresentException
- NoSuchWindowException
- SessionNotFoundException
- StaleElementReferenceException
- InvalidSelectorException
- ElementNotSelectableException
- TimeOutException
Now, we will explain all these Selenium WebDriver Exception in a detailed and practical way:
NoSuchElementException
This Exception occurs when the locators (i.e. id / xpath / css selectors etc) we mentioned in the Selenium Program code is unable to find the web element on the web page. There are two possibilities for getting this Exception, i.e. either we have provided an incorrect locator and trying to find the web element or we have provided the correct locator, but the web element related to the locator is not available on the web page.
Click here to understand NoSuchElementException in a detailed and practical manner.
ElementNotVisibleException
This Exception occurs when the locators (i.e. id / xpath / css selectors etc) we have provided in the Selenium Program code is trying to find the web element that is hidden from displaying on the page. For example, there is no button displayed on the web page and if there is HTML code related to the button, then on trying to find the button using locators of the button by executing the Selenium Code, we get ElementNotVisibleException .
Click here to understand ElementNotVisibleException in a detailed and practical manner.
NoSuchFrameException
iframe is an HTML web page inside another HTML web page. To work with the Web Elements on any iframe, we have to first switch to the iframe in Selenium and then locate the respective web elements inside the iframe. NoSuchFrameException WebDriver Exception occurs when the driver in the Selenium Program code is unable to find the frame on the web page to switch. i.e. when the driver is switching to an invalid or non-existing iframe.
Click here to understand NoSuchFrameException in a detailed and practical manner.
NoAlertPresentException
Alert is a type of pop-up, which pops up to provide important information to users. To work with Alert pop-ups, we have to first switch to Alert and then perform operations on Alert like reading the messages on the Alerts or Accepting the alert by pressing the ‘OK’ button on the alert, etc. NoAlertPresentException WebDriver Exception occurs when the driver in the Selenium Program code is unable to find the Alert on the web page to switch. i.e. when the driver is switching to an invalid or non-existing Alert pop-up.
Click here to understand NoAlertPresentException in a detailed and practical manner.
NoSuchWindowException
As Selenium only automates Web Applications, we will be mostly dealing with Browser Windows. A Browser Window is a square box in which a browser generally displays the web pages in it. In order to work with the Web Elements on any Browser Pop-up Window, we have to first switch to the pop-up in Selenium and then locate the respective web elements inside the pop-up window. NoSuchWindowException WebDriver Exception occurs when the driver in the Selenium Program code is unable to find the pop-up window on the web page to switch. i.e. when the driver is switching to an invalid or non-existing pop-up window.
Click here to understand NoSuchWindowException in a detailed and practical manner.
SessionNotFoundException
This Exception will occur when a driver is trying to perform operations on the Web Application after the Browser is closed.
Click here to understand SessoinNotFoundException in a detailed and practical manner.
StaleElementReferenceException WebDriver Exception
StaleElementRefereneException WebDriver Exception occurs mainly because of page navigations in between the execution of Selenium code. i.e. This exception occurs, when Selenium navigates to a different page, comes back to the same old page, and performs operations on the old page. Technically, it occurs when the element defined in the Selenium code is not found in the cache memory and the Selenium code is trying to locate it. When we define an element on a page using Selenium, Selenium stores it in a cache memory. The element stored in cache memory generally gets deleted when the driver navigates away to another page during Selenium code execution. On coming back to the same old page and then trying to identify the cache-removed element on the old page, we get StaleElementReferenceException as a result.
Click here to understand StaleElementReferenceException in a detailed and practical manner.
InvalidSelectorException
InvalidSelectorException WebDriver Exception is a subclass of NoSuchElementException class and it occurs when a selector is incorrect or syntactically invalid. This exception occurs commonly when XPATH locator is used.
ElementNotSelectableException
This exception comes under InvalidElementStateException class The ElementNotSelectableException indicates that the web element is present in the web page but cannot be selected.
TimeOutException
This exception happens when a command takes longer to complete than the wait time. Waits are mostly utilized in WebDriver to avoid the ElementNotVisibleException error.
Sometimes the test page may not entirely load before the following instruction in the program. If WebDriver attempts to locate an element on a webpage before it has fully loaded, the error ElementNotVisibleException is thrown. Wait instructions have been introduced to avoid this issue.

In summary
Exception handling is a critical component of any Java application or Selenium script. By handling exceptions intelligently, we can create resilient and optimum programming. It is also excellent practice to handle exceptions in a script, which will provide you with a more detailed report when a program fails for whatever reason. An exception shouldn’t be ignored as they break program execution. Adding waits can control some cases like ‘NoSuchElementException‘, ‘ElementNotFoundException‘, and ‘ElementNotVisibleException‘.Selenium and Automation Testing
Selenium is an automation framework that is currently backed by top web browser developers (Google, Microsoft, Apple, Mozilla). It is safe to say Selenium is one of the best ways to automate our web browser for now.
We recently took a Close Look at Selenium Benefits and Disadvantages but also, we made a short list of several Selenium Testing Tools, including free and non-free ones, and then came up with a comparison of two Selenium best ones – Robot Framework and Katalon Studio.
TestQuality thanks to its TestQuality Command Line Interface allows you to upload your automated test results from Selenium to TestQuality. Automated test results may be its output in JUnit XML format, which most test automation tools will provide. Test result attachments and related defects are also supported through test name tags or console outputs. Join now and Try TestQuality for Free!
Source and image's attribution Selenium-By-Arun
